Why Does Your Garden Need Tested Soil?
Plants need soil to grow, but only some need the same type of soil. Every soil varies in nutrients, determining the kind of plant it suits. Some soils might be rich in nutrients, and some might not. In many instances, once nutrient-rich soils become nutrient-deficit due to harvesting methods. At the end of this article hope you will get to know why does your garden need tested soil.
Farmers, gardeners, or people taking their first steps into gardening must test their soil’s nutrient level before planting seeds to grow healthy crops. Soil testing is an effective practice that assesses fertilizer levels and crop yields.
It ensures gardeners use the best fertilizer in prescribed quantities to produce flourishing crops. Whether in home gardens, public parks, or farmlands, soil testing is an effective practice for studying the soil and its characteristics. At the end of this article hope you will get to know why does your garden need tested soil.
What Is Soil Testing?
Soil testing is a tool that studies a soil’s nutrient formation and level. It monitors the soil’s physical and chemical properties and nutrient structure and chemically removes elements, such as potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, copper, and zinc, from the soil. After measuring the soil and lime content, soil specialists check the remaining soil structure to determine the best way of farming and delivering profitable results.
What Are The Goals Of Soil Testing?
Soil testing’s primary goal is to ensure a healthy crop yield. At its core, a soil test assesses the fertility of soils to map an efficient farming technique.
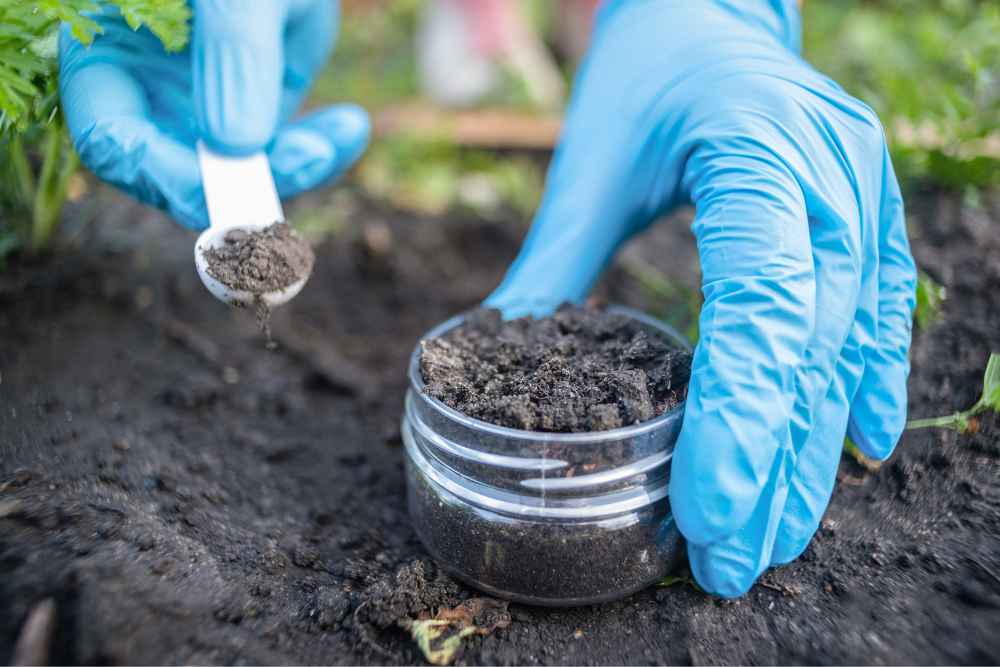

Studying
Soil testing studies the nutrient properties of soil to create a chart of its nutrient availability and needs. Since crop harvesting results in nutrient depletion, soil testing checks the level of fertility.
Assessing
Through soil testing, gardeners determine the soil’s alkaline and acidity issues that might hinder crop and plant growth.
Analyzing
Soil testing generates a report that suggests manure and fertilizer doses according to the soil’s nutrient status and crop requirements. It avoids inadequate or excess fertilizer and chemical use to ensure crop health and practice ecological farming. Soil testing creates a fertilization schedule based on crop needs, soil availability, fertilizer components, and the manure structure.
Evaluating
Soil tests evaluate the compatibility of the soil with the crops. They also conduct periodic evaluations of soil fertility to balance fertilization use and crop productivity.
Increasing Soil Health
Soil analysis enables farmers to restore the soil’s health and healthy for better performance, profits, and long-lasting results.
What Are The Benefits of Soil Testing?
Soil sampling benefits gardeners and their crops in multiple ways. It allows them to study the soil and make informed decisions regarding fertilizer, chemical, and manure use. Soil tests help farmers reduce soil risks, such as nutrient depletion, infertility, erosion, and spoiled lands, and assist them in increasing profits and returns.
With soil testing, gardeners get an accurate estimate of the availability of nutrients in the soil required by the plants and identify incompatible nutrients. Testing the soil determines the soil’s health characteristics, such as the pH level, Electrical Conductivity (EC), Organic Carbon (OC), and Phosphorus (P), which indicate the crop’s performance and sustainability. Soil testing also offers various other benefits, including:
Improving Soil Condition
Crops require fertile soils to grow correctly and remain healthy. A soil’s chemical, physical, and biological components determine its fertility, and measuring these components improves soil fertility. While the naked eye can see physical properties like soil color and structure, analyzing the chemical formation is in a different ballpark. Soil tests measure and determine a soil’s pH level and nutrient status to use the right type and dosage of fertilizers required to improve soil condition.
Cost-Effective Farming
Investing in different fertilizers to check which suits your soil best harms the ground and affects your wallet. Knowing the type of fertilizer required will prevent you from spending money on harmful, incompatible, or unnecessary fertilizers. Furthermore, since elements like potassium and artificial fertilizers have limited availability, their prices skyrocket by the second due to their demand. Therefore, soil sampling allows you to purchase the right fertilizer without wasting resources on the wrong chemicals.
No More Soil Erosion
Soil erosion and degradation are every gardener’s top concerns. According to research, poor soil management results in erosion, harming approximately 24 tonnes of healthy soil. With soil sampling, farmers can create a balanced soil management plan and use the right tools and fertilizers, reducing soil erosion. In addition to preventing soil degradation, soil sampling allows farmers to grow environmentally friendly and economical crops, avoiding expensive and lengthy practices.
Adequate Fertilization
Spraying chemicals and fertilizers on the soil without understanding its structure, components, and nutrients can result in over-fertilization. Soil testing allows you to choose a fertilizer that suits the soil’s components, preventing excess chemical use. Fertilizers protect crops against insects, but exceeding the quantity might harm the crops, causing them to burn and lose their color. Additionally, it can lead to nutrient depletion, soil degradation, low crop sustainability, and soil and water pollution.
Home soil pH tester kits come with vials and tablets to test your soil and a chart to explain the findings. You just put the meter probe into the soil and examine the findings with testing meters.
How To Test Your Soil

A garden trowel, a clean plastic (not metal) container, and a clean bucket are required to prepare a soil sample for sending for analysis. Below are the steps for measuring the pH of soil. Although they are easy to follow, they must be done so carefully to obtain a reliable reading.
- Thoroughly clean the tools that will be used to collect the soil sample.
- Make five 6 to 8-inch-deep holes in the planting area.
- Dip the trowel down about 6-10 inches, and put it in the bucket. For each of the holes, repeat this procedure.
- Gather samples from several locations that will be home to similar plants.
- In the bucket, combine the soil. To dry the soil, spread it out on a piece of newspaper. Take a pint to collect your sample.
To avoid getting a misleading test result, make sure to collect the sample when the soil is mostly dry. To make sure your findings are accurate, you might wish to check the soil more than once.
Soil testing or sampling is essential to conduct healthy and prosperous farming practices. Testing the soil allows you to enhance the soil structure, choose suitable fertilizers, keep the soil healthy, and grow optimum crops.
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024
- 10 Stunning Canopy Bed Ideas for a Dreamy Escape - May 16, 2024