How To Make Soil Fertile Naturally: Unlocking the Secrets
Soil fertility is an important concern for both commercial farmers and home gardeners.
Fortunately, there are techniques for making the soil nutritious so that you may create a wholesome and fruitful garden, whether you are planting veggies for your family or lovely flowers.
What Is Soil Fertility?
It is the capacity of the soil to support plant growth and maximize crop yield. This can be boosted through organic and inorganic fertilizers in the soil. Plants require more nutrients than only nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for growth. They also need calcium, magnesium, sulfur, boron, manganese, chlorine, zinc, iron, copper, and molybdenum, which they typically obtain from the soil.
If any of the nutrients are in limited supply, plants might develop deficiencies and more serious anomalies such as malformed fruits. Certain soils are naturally poor in specific minerals, while others may have been depleted by growing crops in the same region repeatedly without replacing them.
Here we are giving you some ideas on how to make soil fertile naturally using ingredients you find at home.
Factors Affecting Soil Fertility
- Composition of Minerals – The soil’s mineral makeup influences how well it can hold onto plant nutrients. The soil’s quality can be improved by using the right manures and fertilizers.
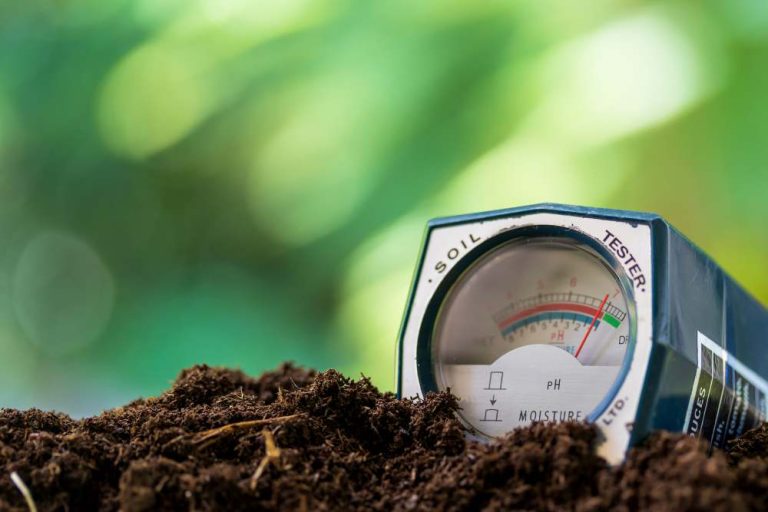
- Soil pH – Soil pH helps to preserve the soil’s nutrient availability. A pH range of 5.5-7 is ideal for soil fertility.
- The texture of the Soil – Minerals of various sizes are responsible for preserving the soil’s structure. Clay soil can hold more nutrients and hence functions as a nutrient reservoir.
- Organic Matter – Organic stuff contains nitrogen and phosphorus. Organic matter can be mineralized and made available to plants.
How To Restore Soil Fertility Of Your Garden

Get the Soil Tested
When you think about infertile soil, you probably imagine soil that has completely lost all of its nutrients. Although this is a problem, there are other factors to take into account.
Furthermore, the soil is home to organisms other than your plants. Several organisms, such as earthworms and beneficial bacteria, help maintain healthy soil. Soil can quickly deteriorate if these organisms are leached out or killed as a result of events such as flooding, erosion, or abnormal pH levels. For instance, even if nutrients are abundant in the soil, plants won’t be able to use them if the pH of the soil is beyond the range that is suitable for the plants you are cultivating.
Before you start changing your soil to restore soil fertility, you must first diagnose the problem. Do a test to see whether the nutrient levels are correct to discover if you have rich soil. The test will determine whether your soil is balanced in terms of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
You have two options for evaluating your soil: either hire an expert or do it yourself using a soil testing kit from a gardening or home improvement store. Most plants survive only when the soil’s acidity and alkalinity levels are balanced. You must add ground limestone if the soil’s pH is too low, or below 5.5 on the scale. If the pH is higher than 7.5, apply soil sulfur.
Employing a drop spreader can assist ensure that either soil supplement is distributed evenly. If you don’t regularly test your soil, a visual inspection is a quick and simple technique to determine its quality. Crumbs of different sizes that retain their shape while being applied with little pressure should make up soil.
If breaking up the crumbs is difficult, this indicates that the soil is excessively hard. It takes time to develop healthy soil for your garden. You perform it consistently throughout the year. You should test your soil periodically for this reason. Moreover, the test will reveal how much potassium, calcium, sulfur, and other nutrients are present in the soil.
Ways Of Making Soil Fertile
The next step is to amend the soil with fertilizer so that the plants can thrive. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus(P), and potassium (K) are the three most important nutrients for plants. The nutrients are represented by the N-P-K label seen on full fertilizer labels.
Some fertilizers contain equal levels of all of these nutrients, while others may be high in one and low in the others. Your plants also require calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and a variety of micronutrients, including iron, manganese, and zinc.
To determine the kind and quantity of fertilizer you need to incorporate into the soil before planting, consult the findings of your soil test. Throughout the growing season, some plants can also require additional fertilizer applications.
Continue to enhance your soil by adding more organic material before planting each year. Soil testing should be done every three to five years, but you can test more frequently if you see your plants struggling. Crop rotation is essential for disease prevention.
1. Compost
Compost is a fertilizer made from decomposed leaves, dried plants, and vegetable waste that can be used to improve the health of garden soil. It also feeds worms and other organisms in the soil while keeping it loose to enhance aeration.
In addition to preventing pests and diseases, it aids in the soil’s ability to retain moisture. Composting is something that you may accomplish on your own. For maximum results, combine one part moist, green elements like kitchen trash with three parts dry ingredients like branches, dried leaves, and so on. Water the compost pile regularly.
Composting is an excellent approach to helping the environment and your garden. Gather all of your natural food waste, including grass clippings, coffee grounds, and vegetable peelings, for your plants rather than dumping it in the garbage.
Composting systems are available for purchase, or you can manufacture compost at home with common things. Compost in your garden gives your plants the beneficial microbes they require to thrive. Spread a three-inch layer of compost evenly over the top of your soil to ensure its effectiveness. It will function as a form of defensive insulation. Composting, in addition to boosting development in your garden, can help keep hazardous insects away.
Frequent applications of small amounts of compost—one-quarter inch every season—can supply slow-release nutrients that will significantly increase your soil’s capacity to retain water and aid in the control of the disease.
2. Mulch The Soil Surface
Mulching is the application of layers of manure or compost to the soil’s surface. It not only contributes to keeping the soil moist, but it also regulates the soil temperature. If done correctly, mulching can considerably improve soil fertility. Mulch provides nutrients to the worms and insects below as it slowly breaks down, maintaining the soil cycle.
You can use a variety of materials as mulch in your garden. There are several excellent possibilities for organic leftovers, including hay, straw, leaves, sawdust, shredded bark, etc. Another effective source of organic mulch is compost created from kitchen leftovers. Mulch can also be made from shredded newspapers, cardboard, and animal dung.
3. Avoid Tilling
Avoid using tilling techniques like shoveling and raking at all costs if you want to keep your soil healthy and productive. While these approaches are beneficial on huge farms, they will destroy the soil in your lawn or garden. It will lose not only nutrients and fertilizers but also the ability to hold water.
The worst-case scenario is that it can promote soil erosion, which would spell the end for your once-beautiful lawn. There are ways to get loose soil for planting without tilling the ground. Without turning the soil over, gradually loosen the top few inches of soil using a digging fork. By doing this, you can avoid damaging the soil’s structure and disturbing the microbiological processes that are taking place there.
4. Plant Cover Crops
Planting cover crops is possibly the most useful method we can use to feed our soil, increase its fertility, and enhance its structure with each passing season. Newly died cover crops supply readily available nutrients to our soil microbial companions, and so to food crop plants.
Moreover, water and oxygen can reach the soil through the pathways that the cover crop roots’ decaying tissues have created. Since they convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms useful to crop plants, legumes including clovers, alfalfa, beans, and peas are particularly excellent cover crops.
Mixes of different cover crops are often beneficial. For example, in mixes of grasses and clovers, the grasses add a large amount of biomass and improve soil structure because of the size and complexity of their root systems. Legumes add nitrogen, which speeds up the breakdown of the relatively carbon-rich grassroots.
Several cover crop mixtures are frequently advantageous. For instance, in mixes of grasses and clovers, the grasses contribute a significant amount of biomass and enhance soil structure due to the size and complexity of their root systems, while the legumes add nitrogen to aid in the fast breakdown of the comparatively carbon-rich grassroots.
Cover crops should be planned with the same care as food crops. The simple solution is to keep two different garden areas: Grow one for food crops and one for cover crops, then alternate the two crops the following year.
Nevertheless, most gardeners cannot devote so much land to such a method, thus good cover cropping must be integrated into a unified garden layout, a concept that may become fiendishly difficult in practice. Cover crops are ideally suited to each of the four seasons and practically any cropping technique.
5. Integrate Rock Phosphate
Vegetables grown in phosphorus-rich gardens will grow larger and healthier. Nickel, iodine, zinc, boron, and other nutrients found in rock phosphate enhance plant growth. You only need a bag of rock phosphate from your local gardening store to spread over your garden.
If you perform this once every two years, you will see a significant improvement in the quality of your plants, fruits, and vegetables.
6. Avoid Harsh Chemicals
You want to keep insects out of your vegetable garden, but some insecticides might harm the soil. Use compost, mulch, and biostimulants instead of insecticides and chemicals. Compounds and microbes are examples of biostimulants. This mixture will lessen your garden’s susceptibility to insects, even though you can’t completely prevent keeping out invaders.
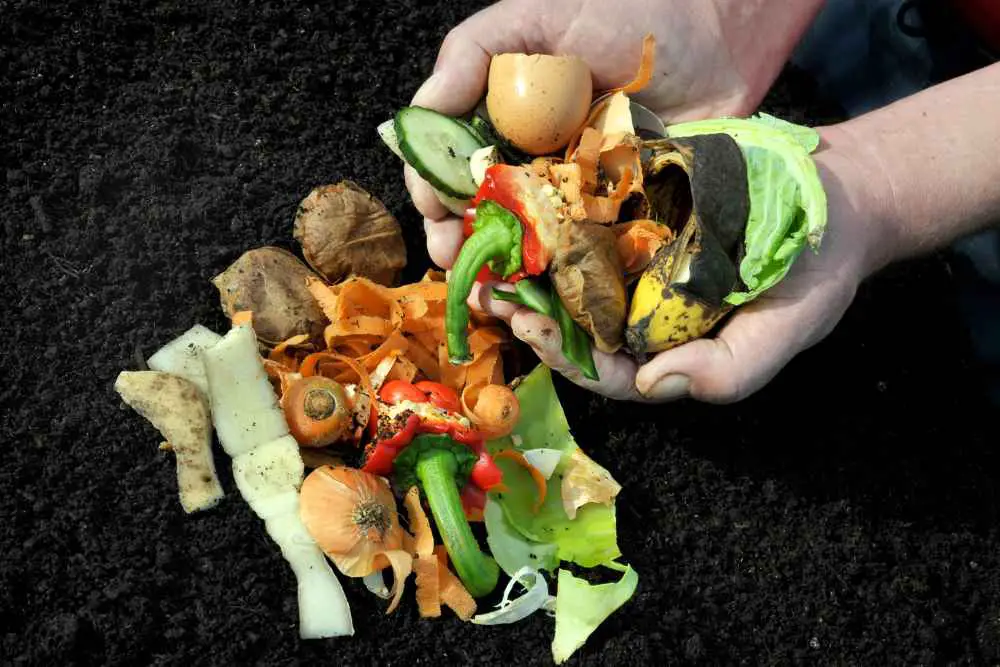
How To Enrich The Soil Using Kitchen Scraps
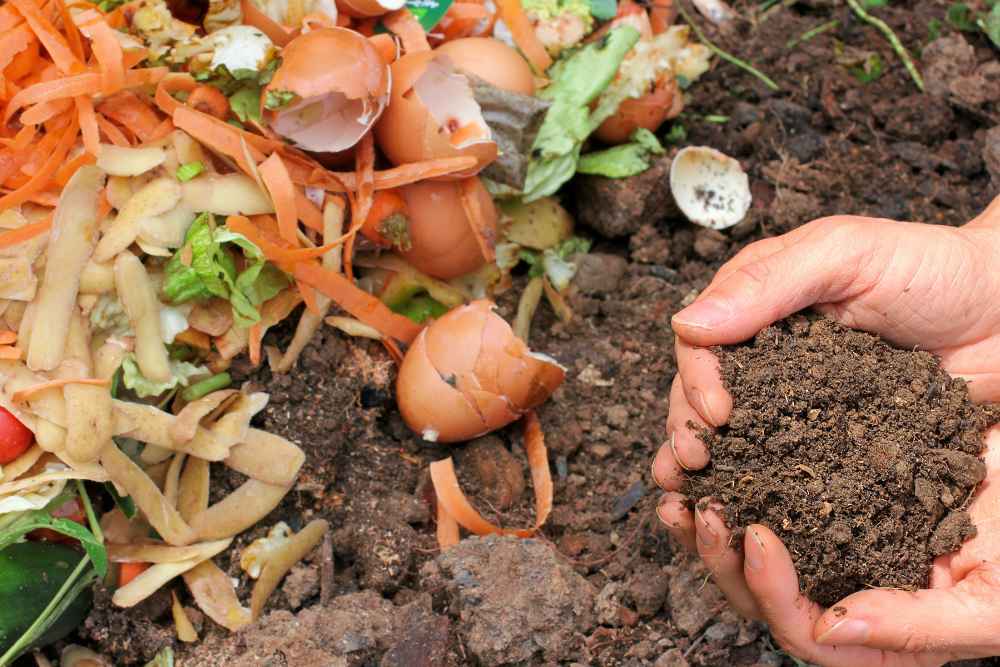

1. Eggshells
Eggshells can be crushed and added to the soil or your vermicompost rather than being thrown out. Your plants will benefit from their nitrogen, phosphorus, and calcium. Even the water used to boil eggs contains calcium. so don’t throw it away.
Let it cool before using it to water your plants. Eggshells are high in calcium, as well as nitrogen, and phosphorus. They work well as a liming source to increase pH levels. Before using the shells, they should be dried and crushed. Simply, smack them with a hammer after placing them in a bag.
Crushed eggshells can be sprinkled around plants to keep cutworms and slugs away and to discourage ants. Alternatively, work a handful of broken eggshells into the soil to improve its nutritious content.
Eggshells are very helpful to vegetables like tomatoes, squash, peppers, and other plants that are prone to blossom end rot. Because eggshells do not break down quickly enough to release calcium, they may not be beneficial to this season’s produce. But eventually, they do break down to directly supply calcium to the soil.
2. Banana peels
Banana peels (and bananas) are high in potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, sulfur, and salt. Because of the potassium content, they form natural fertilizers for roses and other lovely flowers. Just incorporate them into the soil before planting your flowers.
They decompose spontaneously, and the surrounding soil absorbs the potassium. Some gardeners say that throwing full banana peels close to the base of the plant—, particularly around rose bushes—helps the plant produce an abundance of bloom and keeps aphids away, although it looks extremely unpleasant and attracts fruit flies.
Peels should be cut into smaller pieces and buried in the ground rather than being burned. Alternatively, you can fill the bottom of the hole you dig before planting a rose shrub with whole banana peels. Banana peels can also be used as fertilizer by crushing and sprinkling them on top of the soil after air drying them until they are crisp. This will increase the soil’s potassium and phosphorus levels.
3. Coffee grounds
If you like to brew coffee at home, it’s time to start using the coffee grounds to benefit your plants. They aid because they contain nitrogen, which is slowly released into the soil. Other minerals found in it include magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and copper.
Also, coffee grounds promote the growth of microorganisms in the soil, which provides food for earthworms and improves soil structure. Coffee grounds are said to be effective at keeping snails and slugs away from plants, especially around hostas, according to some gardeners.
Coffee grounds can be used as mulch by being applied as a thin layer on top of the soil. This will assist your soil in holding onto moisture after watering. Coffee grounds can also be incorporated into the soil or placed beneath a layer of mulch.
Spread them thinly over the soil, then add some brown or carbon-rich materials to balance them, such as dried leaves, newspapers, and prunings. Coffee grounds do not immediately enrich the soil with nitrogen. Yet, it enriches the soil with organic material to enhance water absorption, drainage, and aeration.
4. Rice starch
Never discard the water used to wash rice. It contains a lot of starch, which helps soil microbes. Moreover, it includes and enriches the soil with trace levels of minerals and vitamins including nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
5. Coconut coir
Save the coconut coir and packaging padding that are included in the egg boxes. It makes excellent mulch, which serves as an additional soil layer to conserve soil, retain water, inhibit the growth of weeds, and enhance aesthetics. It is high in carbon and can be combined with kitchen garbage to make compost.
- 10 Modern Boho Bedroom Ideas to Inspire Peaceful Nights - April 26, 2024
- Bohemian Bedroom Ideas on a Budget | Chic & Affordable - April 24, 2024
- 18 Rose Types and Names for Your Garden - April 23, 2024