Do Succulents Produce Oxygen? A Deep Dive into the Green Lungs of Succulent Plants
Do Succulents Produce Oxygen?” is a common query among plant enthusiasts and eco-conscious individuals wondering about the oxygen-generating capabilities of these resilient plants.
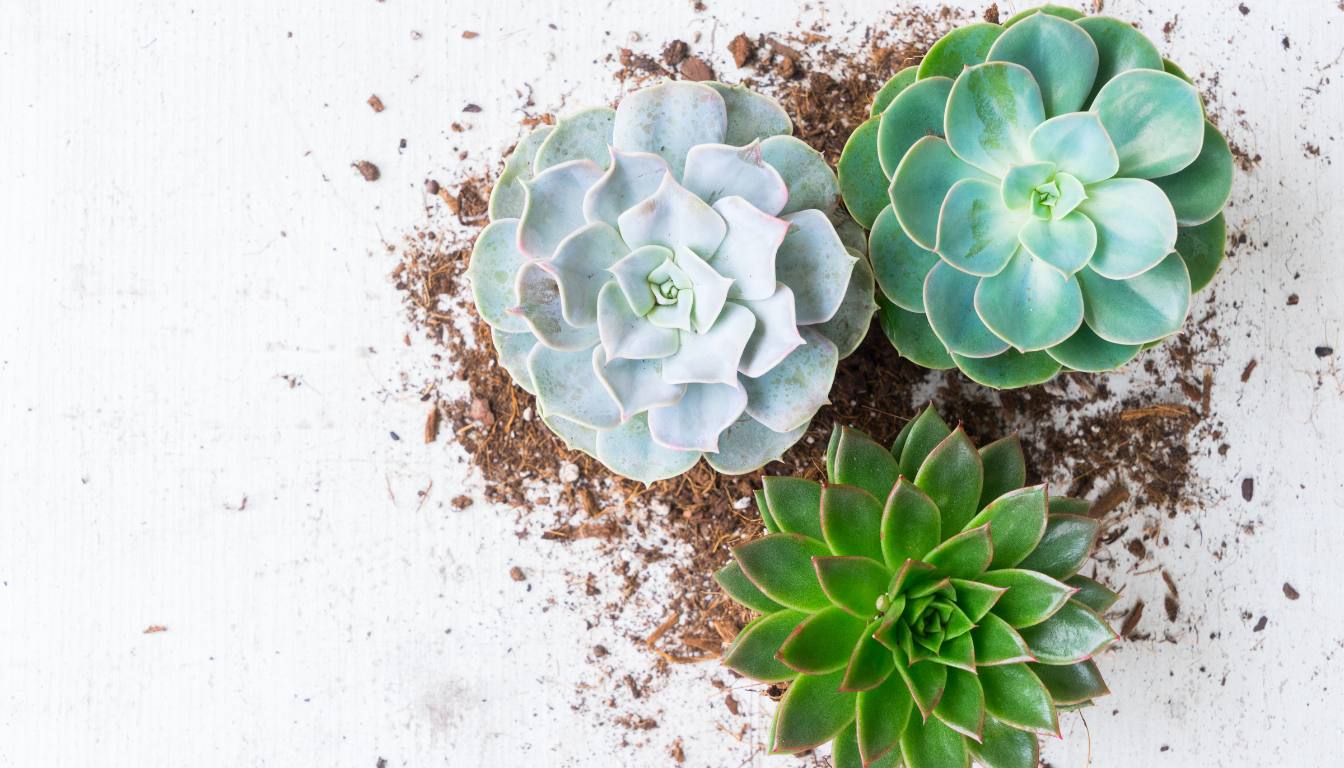
Succulents are a diverse group of plants celebrated for their unique ability to store water in thick, fleshy leaves, stems, or roots, enabling them to thrive in arid and semi-arid environments. This adaptation to water scarcity has not only given them a distinct appearance but also made them resilient and low-maintenance, making succulents a popular choice for indoor and outdoor gardens.
These plants come in various shapes, sizes, and colors, showcasing a stunning array of textures and forms. Their ability to withstand dry conditions has led to the evolution of fascinating characteristics such as rosette formations, intricate patterns, and striking symmetry in their growth patterns.
Examples of Succulents

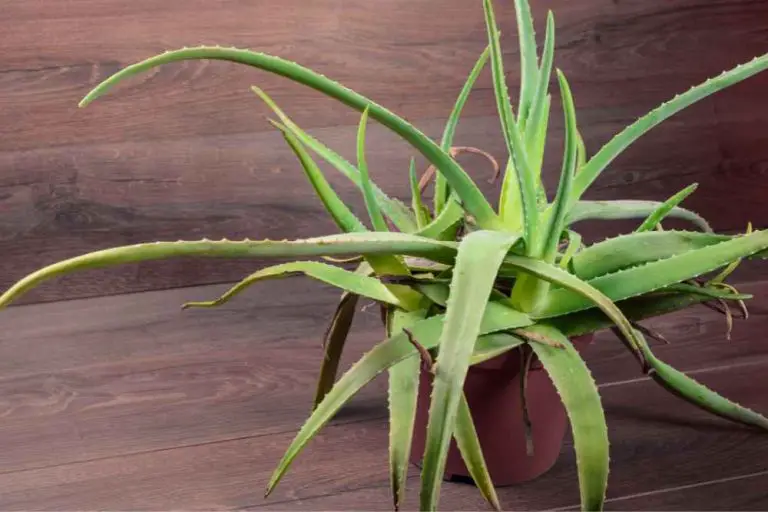
- Aloe Vera : Renowned for its medicinal properties, Aloe Vera is a well-known succulent with thick, fleshy leaves that contain a soothing gel. It’s not only an attractive addition to gardens but also serves as a healing remedy for skin ailments.
- Echeveria: This diverse genus encompasses numerous rosette-forming succulents with unique coloration and leaf structure. Echeverias are popular choices for both indoor and outdoor arrangements, adding a touch of elegance with their captivating symmetry.
- Sempervivum (Hens and Chicks): These charming succulents form tight rosettes and produce smaller offsets, known as “chicks,” around the main plant. Their name, Sempervivum, translates to “always living,” reflecting their hardiness and ability to thrive in various conditions.
- Crassula ovata (Jade Plant): Recognizable by its thick, oval-shaped leaves and tree-like growth habit, the Jade Plant is a classic succulent often associated with good luck and prosperity. It is a popular choice for both novice and experienced succulent enthusiasts.
- Sedum: The Sedum genus includes a vast array of succulents, ranging from low-growing ground covers to tall, upright varieties. They are known for their resilience and are often used in landscaping to provide texture and visual interest.
- Agave: With striking architectural forms, Agave plants are known for their impressive symmetry and spiky leaves. Some species, like the Agave americana, are iconic symbols of arid landscapes and are admired for their sculptural qualities.
- Haworthia: Characterized by their striking architectural rosettes and often intricate patterning on their leaves, Haworthias are compact succulents that make excellent choices for indoor cultivation due to their adaptability to low-light conditions.
- Kalanchoe blossfeldiana: Known for its vibrant and long-lasting blooms, Kalanchoe blossfeldiana is a popular flowering succulent. It produces clusters of colourful flowers above its thick, succulent leaves, adding a burst of colour to gardens and indoor spaces.
- Aeonium: These dramatic succulents form rosettes on the ends of long stems, creating a visually striking appearance. Aeoniums come in various colours and are often grown for their ornamental value.
- Succulent Euphorbia (Euphorbia trigona): Also known as the African Milk Tree, this succulent displays a unique, cactus-like appearance with segmented stems and minimal leaves. It’s appreciated for its sculptural appeal.
Do Succulents Produce Oxygen?
Yes, Like other plants, succulents undergo photosynthesis, a vital process in which they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. While the primary goal of photosynthesis is to produce glucose for the plant’s energy, the byproduct of this process is indeed oxygen. Therefore, succulents, with their unique water-storing adaptations, contribute to oxygen production, albeit in varying amounts depending on factors such as size, species, and environmental conditions.
During daylight hours, succulents open microscopic pores called stomata on their leaves to absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Through a series of biochemical reactions, carbon dioxide is combined with water, using sunlight as the energy source, to produce glucose and oxygen. This oxygen is then released into the atmosphere as a byproduct.
While succulents may not be as renowned for oxygen production as some larger plants, their contribution should not be underestimated. Additionally, the benefits of having succulents in indoor spaces include their ability to thrive with minimal care and their potential to enhance air quality by releasing oxygen while absorbing carbon dioxide.
How Much Oxygen Do Succulents Produce?

Various factors influence the amount of oxygen produced by succulents, and it is generally lower compared to larger plants and trees.
The oxygen production of succulents is determined by their size, growth rate, and the intensity of light they receive. Generally, larger plants and trees have more foliage and conduct more photosynthesis, resulting in higher oxygen production. Succulents, with their often compact and slow-growing nature, may produce less oxygen in comparison.
The specific species of succulent also plays a role. Some succulents, especially those with thicker leaves and stems, may have a reduced surface area for photosynthesis, impacting their oxygen output. However, certain succulents with more extensive foliage or faster growth rates could contribute more significantly.
Light intensity is a critical factor influencing photosynthesis and, consequently, oxygen production. Succulents, adapted to arid environments, can thrive in various light conditions, but their optimal oxygen production occurs under bright, indirect light. In lower light conditions, their photosynthetic activity decreases, affecting the amount of oxygen generated.
While the oxygen production of individual succulents might be relatively modest, the cumulative effect can still contribute to the overall oxygen levels in an indoor or outdoor environment. Furthermore, the benefits of succulents extend beyond oxygen production. They can enhance air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen while also acting as natural air purifiers.
Do succulents That Produce Oxygen at Night?
Most plants, including succulents, primarily release oxygen during the day as a byproduct of photosynthesis. However, there are some specific types of succulents, known as CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) plants, that exhibit a unique ability to perform a variant of photosynthesis at night. This process allows them to release oxygen during nighttime hours as well.
One notable example of a CAM succulent is the Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis miller). Aloe vera is renowned for its gel-filled leaves, which have various medicinal properties. Still, it is also recognized for its CAM photosynthesis, making it one of the few succulents that can contribute to oxygen production during the night. This makes Aloe Vera a fascinating and versatile addition to indoor spaces, not only for its aesthetic appeal but also for its potential to enhance air quality in the evenings.
Another example is certain species of Kalanchoe, such as Kalanchoe daigremontiana, commonly known as Mother of Thousands. This succulent, native to Madagascar, features distinctive, toothed leaves and produces small plantlets along the edges of its leaves. Like Aloe Vera, Kalanchoe exhibits CAM photosynthesis, allowing it to release oxygen at night.
It’s important to note that while these succulents have this unique ability, the overall impact on oxygen levels in indoor environments is relatively small. The primary benefits of keeping succulents, including those with CAM photosynthesis, indoors extend beyond oxygen production. They contribute to aesthetic appeal, help reduce indoor pollutants and can positively influence the psychological well-being of occupants by bringing nature into living spaces.
Do Succulent Plants Purify the Air?

Yes, succulent plants, particularly certain varieties, possess air-purifying capabilities, contributing to the enhancement of indoor air quality. While not as prominent as some larger plants, succulents can effectively filter and cleanse the air by absorbing certain pollutants and toxins.
Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Succulents, including popular varieties like Snake Plant (Sansevieria) and Aloe Vera, have been found to absorb and filter out VOCs from the air. VOCs are emitted by common household items such as cleaning products, paints, and furniture and can have adverse health effects. Succulents can help mitigate the impact of these pollutants by absorbing and breaking down VOCs.
Absorption of Particulate Matter: Some succulents have been shown to absorb particulate matter from the air. This includes dust, pollen, and other airborne particles that can contribute to respiratory issues. The surface of succulent leaves can trap and filter out these particles, leading to a cleaner and healthier indoor environment.
Reduction of Indoor Humidity: Succulents, with their ability to store water in their stems, and leaves release moisture into the air through a process called transpiration. This natural release of moisture can contribute to a modest reduction in indoor humidity levels. Maintaining optimal humidity levels is essential for preventing the growth of mould and mildew, which can adversely affect air quality.
Read – Using a Humidity Tray for Indoor Plants
5 Best Air Purifying Succulent Plants

Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis miller)
Aloe vera is renowned not only for its soothing gel but also for its exceptional air-purifying qualities. This succulent is known to remove pollutants such as formaldehyde and benzene from the air.
Its ability to thrive in indirect sunlight and dry conditions makes it a perfect choice for both indoor and outdoor spaces. The spiky, fleshy leaves contribute to its distinctive appearance, making Aloe Vera a popular decorative and health-conscious addition to homes.
Snake Plant (Sansevieria trifasciata)
Also known as Mother-in-law’s Tongue, is a hardy succulent recognized for its air-purifying capabilities. It excels at filtering out toxins like formaldehyde, benzene, and trichloroethylene.
The Snake Plant is adaptable to various light conditions and is known for its striking, upright leaves that resemble the patterns of a snake. Its resilience and low maintenance make it an excellent choice for beginners seeking an aesthetically pleasing and health-conscious plant.
Spider Plant (Chlorophytum comosum)
The Spider Plant is a popular and effective air purifier, particularly adept at removing pollutants like formaldehyde and xylene. Its arching leaves and offshoots, known as “spiderettes,” contribute to its distinctive appearance.
This adaptable succulent thrives in indirect sunlight and well-draining soil. With its air-purifying abilities and ease of care, the Spider Plant is a favourite for both indoor and outdoor spaces, providing visual appeal along with environmental benefits.
Haworthia Attenuata (Haworthia attenuata)
The Zebra Plant is a striking succulent with distinctive white stripes on its dark green leaves, resembling a zebra’s markings. In addition to its unique aesthetics, the Zebra Plant is known for its air-purifying qualities, helping to filter pollutants like benzene and formaldehyde.
Its compact size and preference for indirect light make it an ideal choice for tabletops or indoor settings where space may be limited.
Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum spp.)
While not a typical succulent, the Peace Lily is a notable air purifier with elegant, lance-shaped leaves and distinctive white blooms. It excels in removing indoor pollutants like ammonia, benzene, and formaldehyde.
The Peace Lily thrives in low to moderate light conditions and prefers consistently moist soil. Its versatility, combined with its air-purifying properties, makes it a popular choice for those seeking a flowering plant that enhances both air quality and visual appeal in their living spaces.
Five Other Benefits Of Succulent Plants
- Water Conservation: Succulents are renowned for their water-storing adaptations, such as thick leaves, stems, or roots, that allow them to thrive in arid conditions. This unique feature makes succulents excellent choices for water conservation, as they can withstand drought and require infrequent watering compared to many other plants.
- Low Maintenance: Succulents are generally low-maintenance plants, making them ideal for both novice and experienced gardeners. Their ability to thrive with minimal care includes resistance to pests and diseases. They often require well-draining soil, infrequent watering, and exposure to bright, indirect light, simplifying the gardening process for those with busy lifestyles.
- Air Purification: Besides oxygen production, succulents, including popular varieties like Aloe Vera and Snake Plant, possess air-purifying qualities. They can absorb and neutralize certain toxins and pollutants from the air, contributing to improved indoor air quality. This feature is particularly beneficial in homes or offices where pollutants from common household items may be present.
- Aesthetically Pleasing: Succulents come in a wide array of sizes, shapes, and colours, making them versatile and visually appealing additions to gardens, landscapes, and indoor spaces. Their unique and often intricate forms add a touch of natural beauty to various environments and are frequently used in decorative arrangements and landscaping projects.
- Adaptability to Various Environments: Succulents exhibit remarkable adaptability to different environmental conditions. From arid deserts to temperate climates, succulents have evolved to thrive in diverse ecosystems. This adaptability makes them suitable for various settings, including homes, offices, gardens, and xeriscaping projects, where their ability to endure different climates and conditions is highly advantageous.
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024
- 10 Stunning Canopy Bed Ideas for a Dreamy Escape - May 16, 2024