Are Galvanized Raised Garden Beds Safe: Pros and Cons
The short answer to this is Yes, galvanized steel raised garden beds are safe
The use of raised beds is growing in popularity. Perfect soil quality is possible with an elevated bed. An elevated bed of good quality may survive for many years, and weeds are easy to avoid. Some are built of brick or rock, while many are made of wood. However, galvanized steel is also gaining popularity as a material.
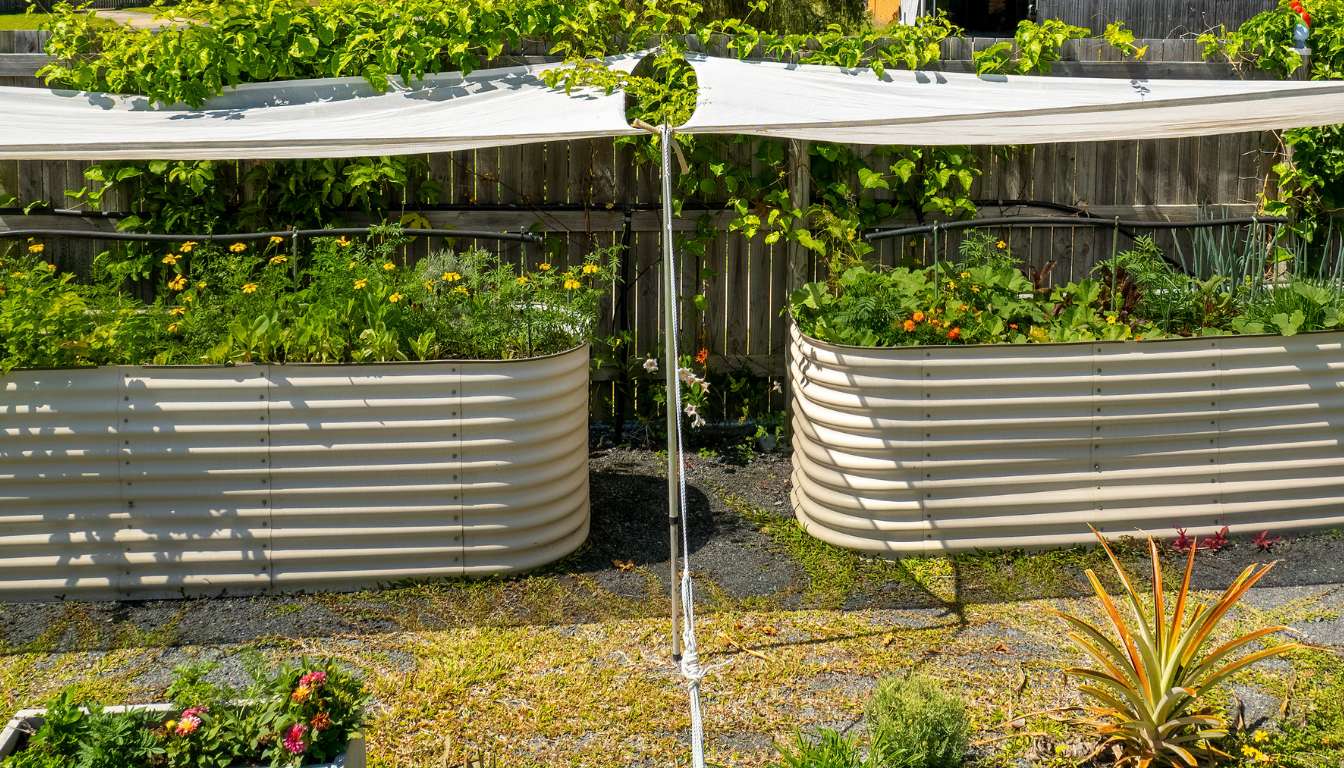
Galvanized raised beds are innovative gardening structures that leverage the durability and corrosion-resistant properties of galvanized steel to create elevated planting containers. These beds have gained popularity among gardeners seeking a reliable, long-lasting solution for cultivating plants, flowers, herbs, and vegetables.
The term “galvanized” refers to the process of applying a protective zinc coating to the steel, which enhances its resistance to corrosion and rust. However, are galvanized raised garden beds safe? Let’s dive in.
What Is A Galvanized Steel Raised Garden Bed?
Galvanized raised beds are innovative gardening structures that leverage the durability and corrosion-resistant properties of galvanized steel to create elevated planting containers.
These beds have gained popularity among gardeners seeking a reliable and long-lasting solution for cultivating plants, flowers, herbs, and vegetables. The term “galvanized” refers to the process of applying a protective zinc coating to the steel, which enhances its resistance to corrosion and rust.
A galvanized raised bed typically consists of panels or sheets of galvanized steel that are assembled to form a rectangular or square container. The sides of the bed are usually held together with bolts or screws, providing stability and structure to the overall unit.
These beds are then filled with soil, creating a contained and well-defined space for gardening. The raised design has several advantages over typical, ground-level gardening, making it an appealing option for both new and experienced gardeners.
Read – Best Soil for Raised Bed Gardening
Is Galvanized Steel Safe For Gardens?
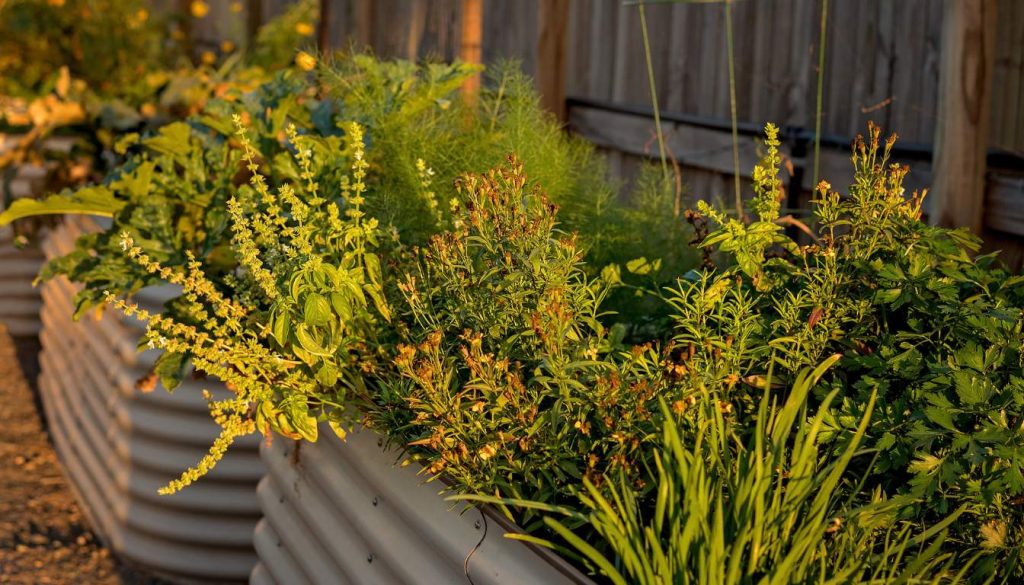

Galvanized steel is widely considered safe for use in gardens, and galvanized raised beds offer numerous benefits for gardening enthusiasts. The safety of galvanized steel in garden applications is primarily due to the zinc coating that protects the steel from corrosion.
Zinc is a naturally occurring element. that is essential for plant growth, and the small amounts that may leach into the soil from galvanized steel are generally not harmful. However, there are some considerations to keep in mind to ensure the safety and well-being of your plants and yourself.
The zinc coating on galvanized steel acts as a barrier against rust and corrosion, extending the life of the metal. This coating also provides a sleek, silver-grey appearance to the raised beds, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. As zinc may gradually leach into the soil over time, it’s important to monitor the pH levels in the soil. While zinc is a micronutrient essential for plant growth, excessive amounts can lead to imbalances in the soil.
To ensure the safety of your garden, regularly test the soil pH and amend it as needed. If pH levels become too high due to zinc leaching, adding organic matter or adjusting the soil with appropriate amendments can help balance it.
If your soil is acidic, add wood ash, lime, bone meal, or ground eggshells to make it alkaline. In general, the risk of zinc toxicity from galvanized steel in raised beds is low, especially when compared to the potential risks associated with other materials like treated wood, which may contain harmful chemicals.
To mitigate the risk of zinc leaching, several precautions can be taken:
- Choose High-Quality Galvanized Steel: Choose raised beds made from high-quality galvanized steel. These products usually have a thicker and more durable zinc coating, reducing the likelihood of leaching.
- Allow Weathering: Allow the galvanized steel to weather for a few months before planting. This process can further minimize the potential for zinc leaching as the initial weathering helps stabilize the coating.
- Use Food-Safe Products: If growing edible crops, choose galvanized steel products explicitly labeled as food-safe. This ensures that the materials used in the galvanization process are safe for contact with plants intended for consumption.
- Consider Using a Liner: To provide an additional layer of protection, some gardeners opt to use a food-grade liner inside the raised bed. This acts as a barrier between the soil and the galvanized steel, preventing direct contact.
- Monitor Soil Conditions: Regularly monitor the soil conditions, including pH and nutrient levels. Which ensures they are within the optimal range for plant growth. This practice helps maintain a healthy and thriving garden.
For those growing edible crops, selecting a galvanized steel product labeled as food-safe or using a barrier, such as a food-grade liner, can provide an extra layer of assurance. Monitoring soil conditions, including pH and nutrient levels, will help ensure a healthy and thriving garden.
Advantages of Galvanized Raised Beds over other Materials like Woods
The advantages of galvanized raised beds over other materials, such as wood, are multifaceted. One of the primary benefits is durability. Galvanized steel is known for its resilience in the face of environmental elements.
The zinc coating acts as a protective barrier, which prevents the steel from rusting or corroding, even when exposed to snow, rain, or sunlight. This durability ensures a longer lifespan for galvanized raised beds compared to wooden alternatives, which may succumb to decay and deterioration over time.
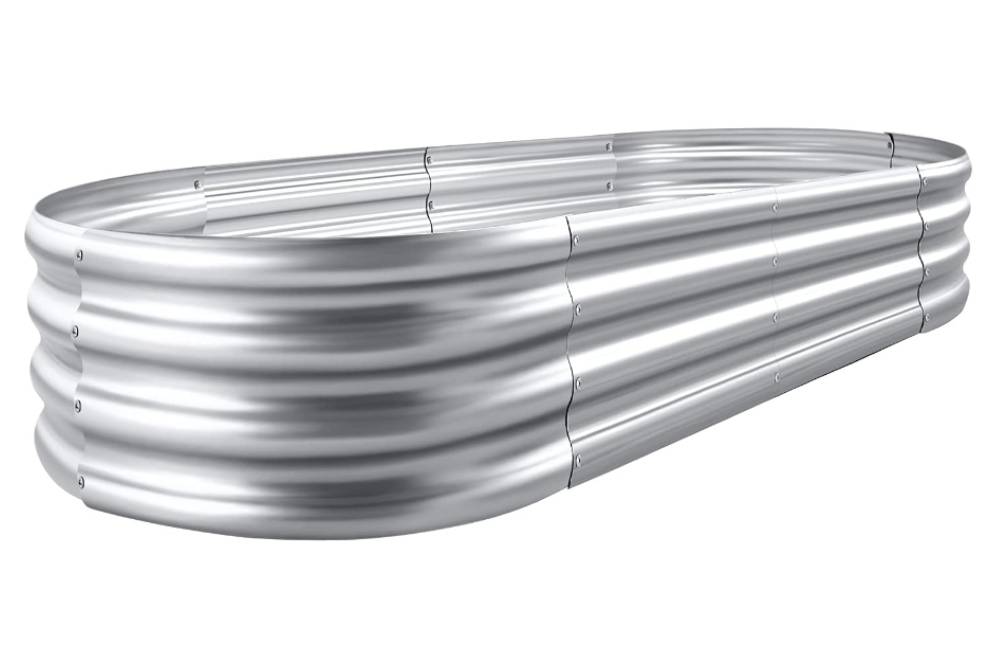
Longevity is a key consideration for gardeners investing time and effort into their gardening infrastructure. Galvanized raised beds offer a robust solution, maintaining their structural integrity and appearance and structural integrity and for years with minimal maintenance required. This is particularly advantageous in regions with variable weather conditions, as galvanized steel can withstand extreme temperatures without compromising its functionality.
Stability is another notable advantage of galvanized raised beds. The inherent strength of galvanized steel provides a sturdy framework for the raised bed, preventing warping, bowing, or shifting of the sides. This stability is crucial for larger or deeper beds, where the pressure from the soil could compromise the structure. Gardeners can have confidence in the reliability of these beds, ensuring a secure environment for plant growth.
The versatility of galvanized raised beds is evident in their ability to cater to various gardening needs. They come in an array of sizes and shapes, allowing for customization based on the available space and the gardener’s preferences. Whether constructing a small herb garden on a balcony or a sprawling vegetable patch in the backyard, galvanized raised beds offer flexibility and adaptability.
Temperature regulation is an often-overlooked benefit of galvanized raised beds. The reflective properties of galvanized steel help manage the temperature of the soil within the bed. This is particularly advantageous in regions with extreme weather conditions, as the reflective surface minimizes heat absorption, preventing the soil from becoming excessively hot. This regulated temperature contributes to optimal growing conditions for plants.
Aesthetically, galvanized raised beds add a modern and clean look to any garden. The silver-grey appearance of the galvanized steel complements various outdoor aesthetics, providing a sleek and contemporary touch. This visual appeal is a significant factor for gardeners who view their gardening space as an extension of their overall home design.
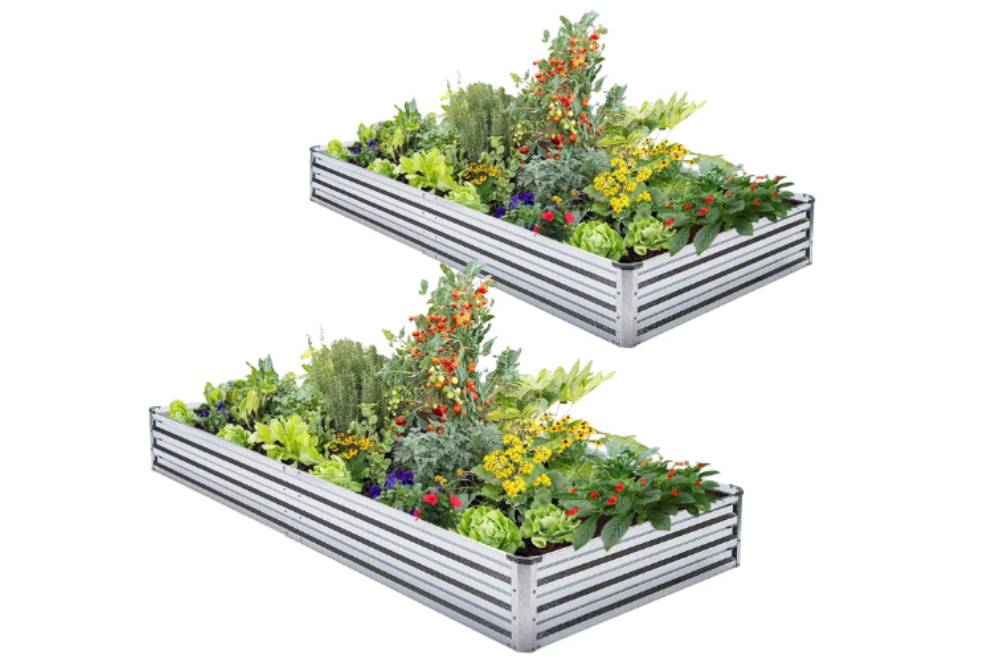

Moreover, galvanized raised beds offer an environmentally friendly choice. Unlike treated wood, which may leach chemicals into the soil, galvanized steel is inert and does not introduce harmful substances to the growing environment. This is especially important for cultivating edible crops in their raised beds, ensuring a safe and healthy harvest.
Maintenance is often a consideration when choosing gardening materials. Galvanized raised beds require minimal upkeep compared to wood. They are easy to clean and can be hosed down if necessary. The absence of the need for staining, sealing, or regular maintenance makes galvanized raised beds a practical and low-maintenance solution for busy gardeners.
Galvanized raised beds are typically easy to assemble and disassemble. This feature is advantageous for those needing to relocate their gardens or adjust the layout. They are also accessible to gardeners of all skill levels because of the ease of assembly.
Galvanized steel’s versatility extends to its adaptability to different gardening needs. Whether you’re creating a small herb garden on a balcony or a large vegetable plot in the backyard, galvanized raised beds can be customized to suit your space and preferences. are galvanized raised garden beds safe
Galvanized raised beds come in various shapes and sizes, offering versatility in design. Whether you prefer a traditional rectangular bed, a modern square design, or even custom shapes, galvanized steel allows for creative and personalized gardening layouts.
Unlike wood, which may attract pests or succumb to decay, galvanized steel is resistant to both. This feature contributes to reducing the likelihood of structural damage caused by insects or fungal growth and a healthier gardening environment.
The reflective properties of galvanized steel contribute to effective temperature regulation within the raised bed. This helps create an optimal environment for plant growth and prevents the soil from becoming excessively hot, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Galvanized steel is a recyclable material, making it an environmentally friendly choice. When eventually replaced, the steel can be recycled, reducing the overall environmental impact compared to materials that may end up in landfills.
How do you Maintain Galvanized Raised Beds in Different Climate Conditions?
Maintaining galvanized raised beds in various climate conditions involves understanding the challenges posed by different weather patterns and taking appropriate steps to preserve the integrity of the metal and the well-being of your plants.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Regularly inspect your galvanized raised beds for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the surfaces with water and a mild detergent to remove dirt and debris, which can accelerate the corrosion process.
- Rust Prevention: While galvanized steel is resistant to rust, scratches, and abrasions can compromise the protective coating. Touch up any exposed metal with galvanized paint to prevent rust formation.
- Drainage: Ensure proper drainage in the raised beds, especially in areas with heavy rainfall. Poor drainage can accumulate water around the metal, potentially accelerating corrosion. Use a well-draining soil mix and consider adding drainage holes if necessary.
- Winter Protection: In cold climates with common freezing and thawing cycles, raised beds can be exposed to additional stress. Consider adding a layer of mulch to protect the soil and roots from extreme temperature fluctuations. This helps minimize the potential for frost heaving, which can impact the stability of the raised bed.
- Elevated Beds: If your region experiences heavy snowfall, elevated beds can prevent the weight of the snow from directly impacting the sides of the bed. This reduces the risk of deformation or damage during winter months.
- Coating Maintenance: Periodically check the condition of the galvanized coating. If you notice any areas where the coating has worn off, consider applying a galvanized spray or paint to those spots to maintain the protective barrier.
- Adjust Soil pH: Regularly monitor the pH levels in the soil to ensure that any potential leaching of zinc does not lead to an imbalance. Adjust the soil pH as needed by incorporating appropriate amendments.
- Protecting Plants: Some plants may be more sensitive to zinc levels than others. If you notice signs of stress or nutrient imbalances in your plants, consider choosing varieties more tolerant of zinc or adjust your soil amendments accordingly.
- Mulching: Mulching around the base of the raised bed helps regulate soil temperature, retain moisture, and prevent weeds. It also provides a buffer between the galvanized steel and the soil, reducing direct contact and potential leaching.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep a watchful eye on the condition of your galvanized raised beds throughout the year. Early detection of any issues allows for prompt intervention, ensuring the longevity of the beds and the health of your plants.
- Choosing the Right Size and Thickness: Consider the size and thickness of the galvanized steel when purchasing raised beds. Thicker steel generally offers more durability, and selecting an appropriate size can prevent overloading and stress on the material.
- Placement and Sun Exposure: Pay attention to the placement of the raised beds concerning sun exposure. While galvanized steel is resilient, prolonged exposure to intense sunlight can contribute to heating, affecting soil temperatures. Proper positioning can mitigate this.
- 29 Bucket Gardening Ideas for a Lush, Compact Garden - October 30, 2024
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024