Sunflowers Gardening: A Comprehensive Guide to Growing Sunflowers
Sunflowers are a favorite among gardeners. They make lovely cut flowers, and their seeds (and oil) provide food for both birds and people! Everything from growing sunflowers to harvesting can be found in our Sunflower Guide.
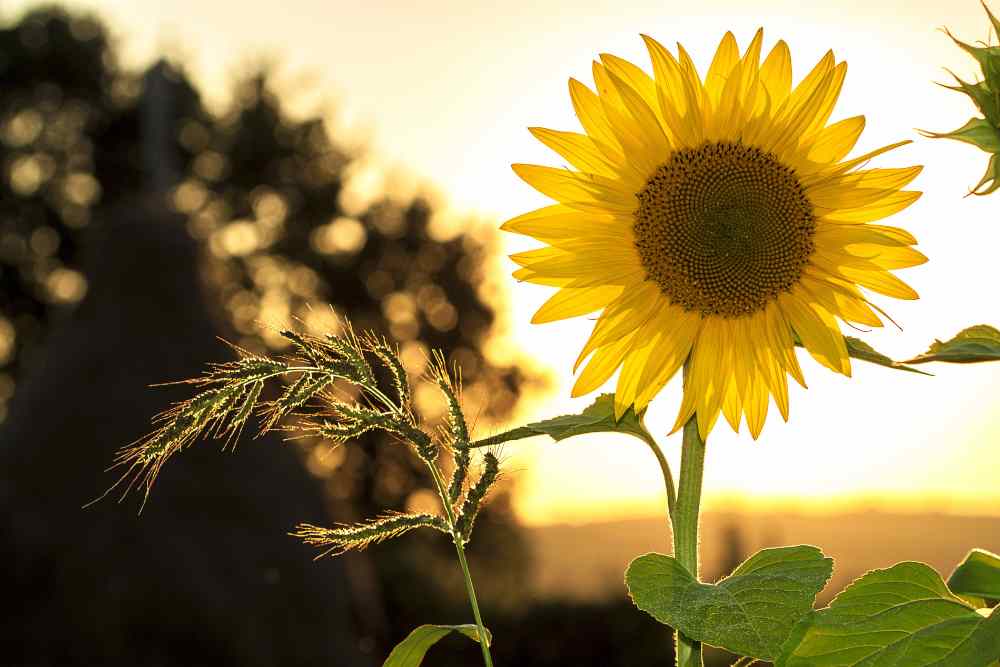
Helianthus annuus, a sunflower is an annual flowering plant with a large daisy-like flower face. The sight of a sunflower blooming in a garden signifies the arrival of summer. Sunflowers, which are native to North America, have been cultivated for thousands of years as a source of food, oil, medicine, and dye, as well as for their beauty.
The flowers come in a variety of colors (yellow, red, orange, maroon, and brown), but the most common are bright yellow with brown centers that ripen into heavy seed heads. Sunflowers are heliotropic, which means that their flowers turn to follow the Sun’s movement across the sky from east to west, and then turn back to face the east at night to prepare for the morning sun. Heliotropism occurs in the early stages of flower development before the flower becomes overburdened with seeds.
Sunflower Varieties
Sunflowers are typically grown in two varieties: oil seed sunflowers and confection sunflowers. Sunflower oil and birdseed are the main products of oilseed sunflowers. Sunflower oil is low in saturated fats and therefore very healthy.
Birds and mammals are attracted to the oils in the seed and will readily eat them, so black Peredovik oil types are best for those primarily planting for wildlife. Confection sunflowers have a large seed coat with black stripes and produce large seeds on large heads. This variety is primarily grown for human consumption, and the seeds are usually roasted or salted and baked.
– Russian Mammoth
The traditional giant sunflower is an aptly named variety that can grow to be more than 12 feet tall with blooms the size of dinner plates. This variety is ideal for seed production. Its seeds can be used as snacks for humans or birds.
– Teddy Bear
It is a small variety that only reaches a height of 2 feet. Therefore it is perfect for small gardens and containers. It has 6-inch wide soft, fluffy gold blossoms that make good-cut flowers.
– Autumn Mix
Sunflowers are tall growers (6 feet or more) with large flower heads that come in a rainbow of fall colors.
– Autumn Beauty
It is a stunning cultivar with branching stems of yellow, orange, bronze, and red blooms. Plants that grow to 6 feet tall produce blooms that are 4″ to 6″ across.
How To Grow Sunflower
Choose a Sunny Spot
Sunflower seed planting is a simple and quick process. You give these plants the best possible start by taking the time to choose the right location and prepare the soil.
Sunflowers are annual plants that grow quickly and thrive in full sun(six to eight hours of direct sun per day). They can be planted individually in landscape beds, but they’re also commonly used in vegetable gardens in rows.
Sunflowers can be started indoors for transplanting, but direct seeding into the soil is a simple way to get them started. Sunflowers should be able to grow in any soil that isn’t constantly waterlogged. Sunflowers thrive in slightly acidic soil, with a pH of 6.0 to 6.8. It’s best to conduct a soil test before planting to determine your soil’s nutritional requirements.
Sunflowers are heavy feeders, so they’ll grow and produce the most blooms in nutrient-rich soil that have been amended with compost or other organic matter. Sunflowers grow best in temperatures between 70 and 78 degrees Fahrenheit.
They are heat tolerant as long as their moisture requirements are met. They can also withstand chilly but sunny conditions. They can also withstand high humidity, but they require well-draining soil and adequate air circulation to avoid root rot and other diseases.
When To Plant Sunflowers
Sunflower seeds usually plant from early March to mid-May. This time varies depending on the variety. Always check the seed packet before planting. The seeds will need to be protected until they’ve germinated and seedlings are around 5cm tall to give them the best start; it’s best to do this indoors to avoid frost damage.
Preparing The Soil

Loosen the soil to a depth of at least 10″, then add compost and/or slow-release organic fertilizer to ensure a consistent supply of nutrients. To make a smooth seedbed, rake the soil.
Growing Sunflowers From Seeds

The majority of sunflowers are grown from seed. Seeds can be planted directly in the garden once the threat of frost has passed in the spring, or they can be started three to four weeks indoors before transplanting to the garden.
Sunflower seedlings should be started indoors in peat or paper pots that can eventually be planted directly into the ground, as their roots don’t like to be disturbed.
Sunflowers require a variety of planting depths and spacing. Your specific sunflower cultivar will determine how to grow sunflowers from seed and how deep to plant sunflower seeds. Sunflower seeds should be planted at least 1/2 inch deep.
Seeds should be spaced 6 inches apart. If you’re going to plant in rows, leave 2 to 3 feet between each row. Plants should be thinned out to the proper spacing in a few weeks. Sunflower seedlings will sprout in 10 to 14 days if the soil temperature is just right.
Sunflower seeds need a lot of space to grow. Plant three seeds in each 3- to 4-inch peat pot to start sunflowers indoors. The best drainage will come from a soilless planting medium. Indoor germination of sunflower seeds takes 6 to 10 days on average. By planting seeds every couple of weeks, you can enjoy continuous blooms throughout the summer. You’ll have beautiful sunflower blooms until the first frost of the fall season if you plant them in succession.
Thin The Seedlings
Then the sunflower seedlings to the recommended row spacing for your variety once they have their first set of true leaves. Small sunflowers only require 6 inches between plants, whereas large varieties require up to 3 feet.
For garden aesthetics, closer spacings are possible, but crowded plants will produce smaller flowers. One seedling per cup should be used for indoor sunflower seedlings. Simply pick the most powerful sunflower and pinch the others back.
Harvesting Sunflower Seeds
Different varieties of sunflowers will grow at different rates. It takes between 80 – 120 days for a plant to mature and develop seeds.

Don’t Let The Birds Eat Your Harvest!
Early in the fall, start checking for seed maturity. As the flower petals dry and fall out, the seeds will begin to face the ground. Simply cut off seed heads with a generous amount of stem attached once they’re ready. Keep away from rodents and insects in a warm, dry location.
Harvest the seeds after the back of the sunflower head has turned brown. Although mature seeds can be picked out earlier, the browning of the head makes removal easier and faster. As the flower heads dry, the seeds fall out naturally. Place netting or a paper sack with air holes over each head to catch as many seeds as possible.
Seeds are easy to remove once completely dry. To dislodge the seeds, take a sunflower head in each hand and rub their faces together. Alternatively, you could simply brush the seeds out with your hands or a stiff brush.
Refrigerate sunflower seeds in airtight glass jars to keep them as fresh as possible. Moisture levels are kept low as a result of this. Consider adding desiccant packages to absorb excess moisture if stored outside of the refrigerator. To encourage air circulation, many people store raw seeds in cloth bags in dark, dry areas.
Cutting Sunflowers For Bouquets
To encourage side blooms in indoor bouquets, cut the main stem just before the flower bud opens. Early in the morning, cut the stems. Flower wilting can occur if flowers are harvested in the middle of the day.
Handle sunflowers with care. In water at room temperature, the flowers should last at least a week. Sunflowers should be placed in tall containers that can support their heavy heads, and the water should be changed daily to keep them fresh.
Sunflowers Common Pests & Diseases
Sunflowers are susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases. The seeds are particularly popular with birds and rodents. Cover the flower heads with netting to protect them from pests if you want to save seeds for planting. Furthermore, the sunflower moth lays its eggs on the plant, and the larvae feed on the flower heads, tunneling into the seeds and leaving holes. Pesticides can aid in moth control.
You might also have problems with beetles or caterpillars eating your foliage. Powdery mildew, downy mildew, and rust are the main fungal diseases that can affect sunflowers. To avoid diseases like this, make sure your plants have enough air circulation and use a garden fungicide as soon as you notice the first signs of infection.
- 15 Ingenious Kitchen Garden Ideas to Cultivate Freshness Right at Home - April 7, 2024
- 10 Top Picks Best Plants for Open Terrarium - April 2, 2024
- 21 Easy and Cheap Walkway Ideas for a Charming Garden - March 31, 2024