Rose Gardening Tips for Beginners: Cultivating Your First Beautiful Garden
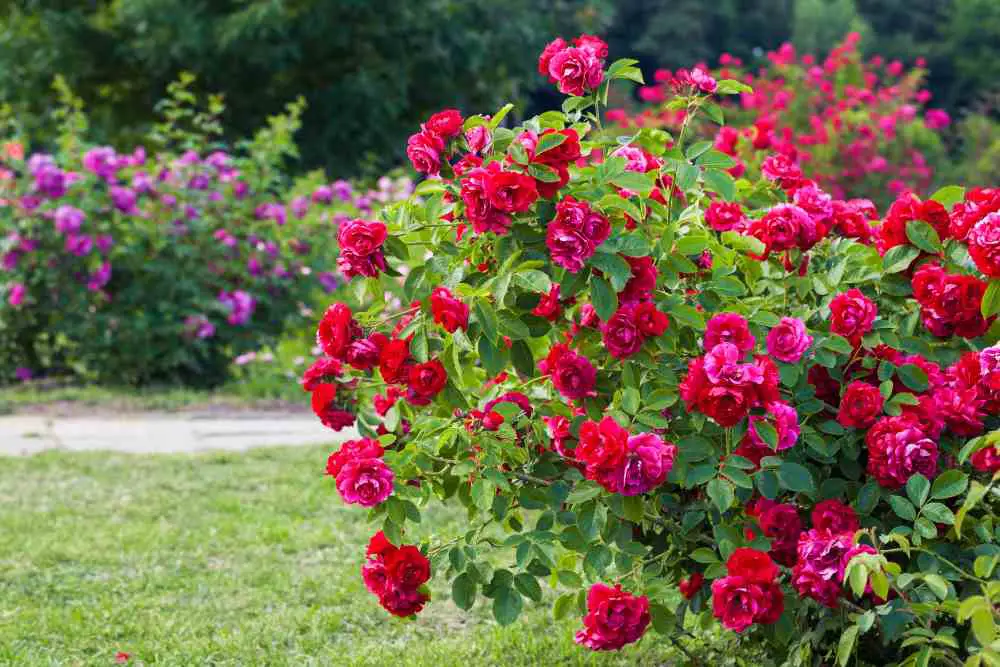
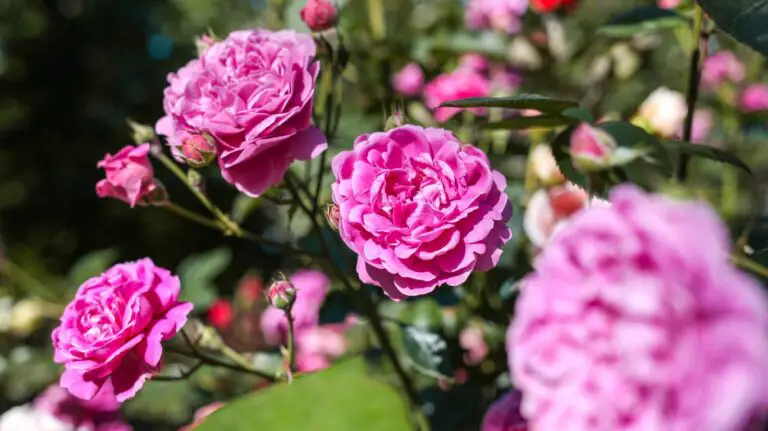
Roses are the most beloved garden plants and also hold a symbol of love, romance, and friendship throughout the world. So, why not start your own magical rose garden? Roses come in different sizes and colors. There are many varieties of roses you can grow in your garden. Select types of roses that are low maintenance, hardy, and resistant to diseases.
For successful rose gardening, you don’t need a formal rose garden to appreciate roses’ beauty; there are many ways to incorporate them into your yard. In this article we will talk about 7 rose gardening tips for beginners.
Types of Roses
Roses are classified into three types based on their growth characteristics: climbing, bush, and shrub.
Climbing Roses
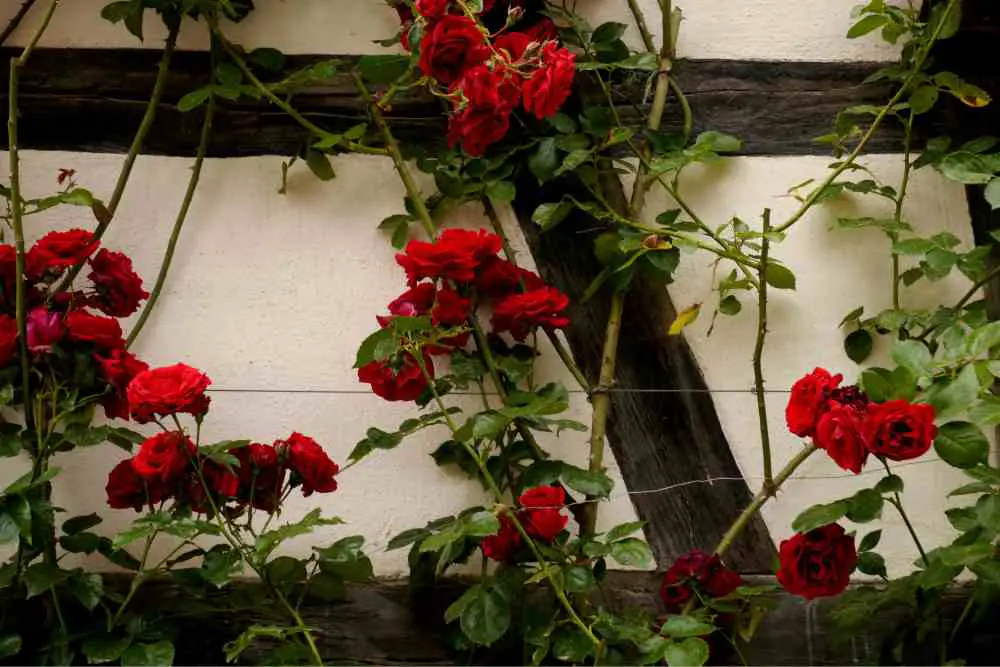

Climbing roses are strong plants with long branches that need to be supported. Branches\canes can be trained to grow along a trellis or fence, or they can be left to sprawl as a bank cover. Depending on the type of rose and how it is supported and maintained, branches can be anywhere from 5 to 20 feet long.
Some are grafted, while others are grown from seed. Climbing roses are also classified into groups according to their flowering and growth habits. Examples; Everblooming climbers, Trailing roses, and Rambler roses.
Bush Roses
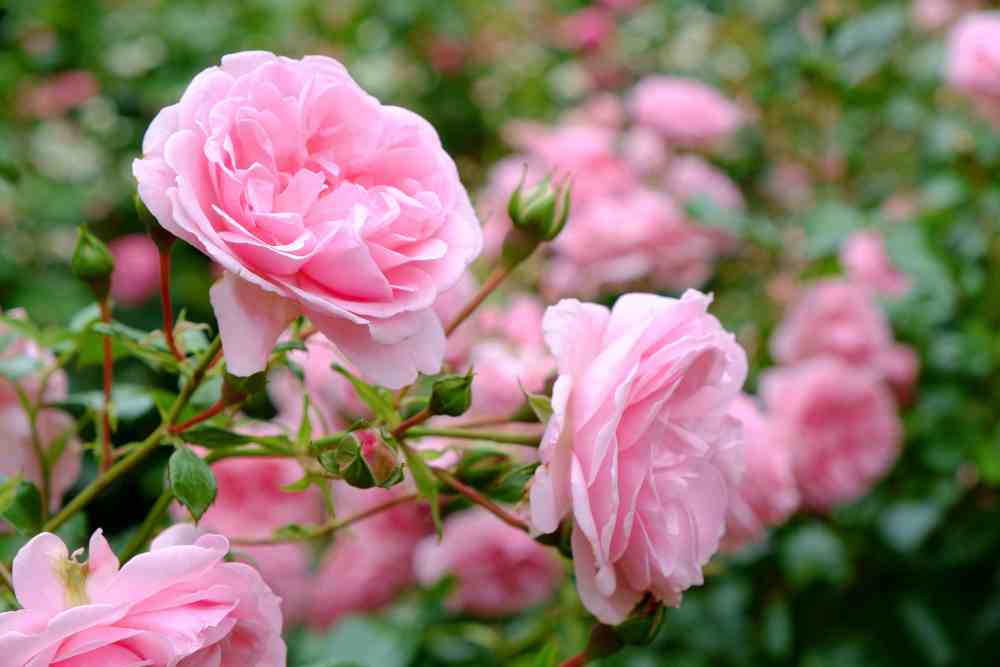

Bush roses are self-sufficient and produce blossoms mostly at the plant’s top. In bush roses, plant heights vary from a few inches to 6 feet. They are further classified based on their development and blooming behaviors. Examples; Hybrid perpetuals, Hybrid teas, Miniature rose plants, Grandiflora, and Floribunda roses.
Shrub Roses
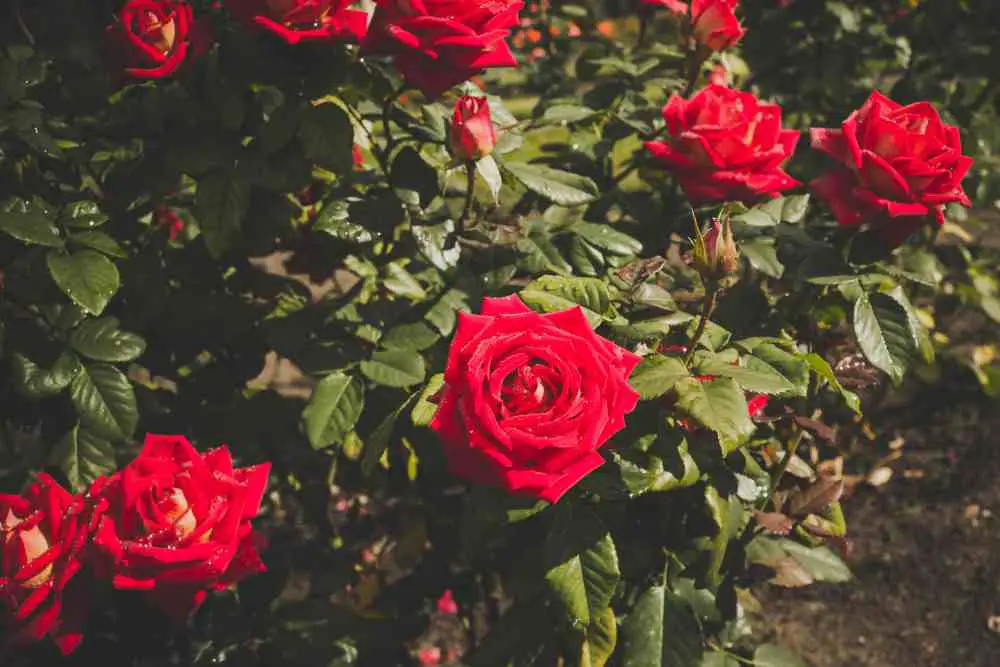

Shrub roses are a diverse group of natural species, hybrids, and cultivars that generate large, dense growth while requiring little care. Many of them have a fine-textured leaf that makes them ideal for use as hedges or screen plants.
7 Rose Gardening Tips For Beginners
Site Selection
Select a location with well-drained soil with a slightly acidic pH between 6.0-7.0. but you can incorporate some well-rotted compost or manure before planting. You can prepare a raised bed or choose a large pot where you can control soil type and enhance drainage. Soils containing excessive amounts of alkali salts or other harmful chemicals are not recommended for roses.
To prepare your soil, dig in a lot of manure before planting. Most of the varieties prefer sunny locations (6 hrs or more) where they are sheltered from strong wind. Do not plant them under trees.
They can grow in the shade, although they are more vulnerable to mildew thrips than plants planted in full light. When the temperature rises above 35°C in the summer, several types stop blooming. Prepare beds/plots that are 1-1.5m broad and 30-40m long.
Time Selection
The ideal time to plant the rose is during the first hint of spring. You can plant bare-root roses or container-grown rose plants now and have flowers by the beginning of summer. The new rose plant will have the whole winter to settle in and establish itself. So when spring finally shows up, they are ready to start growing, and you may even get blooms earlier on in the year.
Plant Selection
Choose roses that are easy to care for and hardy in your area. You can choose colors that you like and that will assist the house blend in with the surroundings.
Roses should be purchased from trustworthy sources like garden centers, nurseries, or mail-order companies. When ordering plants by mail, make sure to order ahead of time so that they arrive in time for planting. Department stores and supermarkets may also have good plants provided their stock has been kept dormant and protected from drying.
Roses can be purchased as bare-root plants or as potted plants. Bareroot roses are frequently sold as packed roses. Rather than soil, they have their roots packed in moisture-holding media like peat moss. When the packing material is removed, the roots become visible. Only a limited amount of bare-root stock can be planted in the early spring.
Before the plants may produce shoots, they must be planted in the ground. Before planting, bare-root plants may need to be pruned. Many distinct cultivars of bare-root roses are commonly sold. Potted roses are great for the casual home gardener who just wants a few plants and likes to plant in the spring.
Hassett Plant Centre offers free, friendly support when it comes to choosing the right plant for your garden. Hassett Plant Centre is a specialist garden center in Northampton, providing a wide range of bedding plants, shrubs, climbers, and hedging. Get in contact with them for support in choosing the right plant for your garden.
Bed Preparation
Planting beds should be prepared at least a month in advance of the planting date. The beds are prepared to a depth of 60-75 cm, and a 45-60 cm wide trench is dug to a depth of 30 cm.
Planting
- Before planting, remove the top 30 cm of topsoil from the trenches. The planting distance is determined by the type of roses and the area. A 60 x 30 cm gap is recommended. For the cultivation of cut flowers, Roses are typically planted at 60 x 60 cm spacing.
- The planting hole must be deep and wide enough to accommodate the roots of the plant. Because roses don’t like moist feet, the location must have sufficient drainage.
- Mix the dirt that was removed from the planting hole with a generous amount of garden compost, peat moss, or other organic materials. Place a small amount of this mixture in the bottom of the planting hole before inserting the rose shrub.
- In mild regions, the plant’s crown should be at ground level. In cold areas, it should be 2 to 3 inches below ground level.
- After that, partially fill the hole with the soil mixture and add a slow-release fertilizer before watering thoroughly. After that, finish filling the hole with the rest of the earth.
- Water once more, then mound loose earth over the rose’s branches to protect it as it adjusts to its new location.
- If you’re planting many rose bushes together, make sure to plant them at least 3 feet apart to give them enough space to expand as they mature.
Water your roses well and place a thick layer of mulch around each plant. Water fresh roses every 2-3 days, especially if the weather is dry until the plants establish themselves. When the plant begins to put forth new growth, you’ll know they’re established. Once your plant has reached this stage, you may proceed to the standard rose bush management indicated below.
Pruning

Roses should be trimmed to eliminate weaker and dead wood and to enhance their look. Pruning is also necessary for controlling the quality and number of flowers produced. To cut branches, use only sharp cutting instruments such as pruning shears or a fine-toothed saw.
Remove dead, broken, weak, or extra branches by cutting close to the spot on the crown where they originate, leaving no stubs behind. Make a 45° angle cut just above a bud that faces the direction you want fresh shoots to develop to reduce long stems.
Maintenance
Watering promotes the development of a deep, robust root system that will support all of those lovely blossoms. During the growing season, feed your bushes with a granular fertilizer sprinkled into the soil every six weeks.
Feeding should be stopped six weeks before the first frost date, and watering should be stopped once the ground freezes. Continue to water the shrub if you live in a frost-free region. This is also a time to remove any dead or diseased branches.

For more information on roses and how to care for them, consult an expert at your local nursery or garden center.
- 29 Bucket Gardening Ideas for a Lush, Compact Garden - October 30, 2024
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024