Guide To Growing Strawberries In Pots – Complete Guide
Strawberries aren’t the easiest crops to cultivate in containers, but it is possible if you follow a few simple guidelines. We’ll show you how to start growing strawberries in pots to ensure a big yield in this article.
Can You Grow Strawberries In Pots?
Strawberries can be grown in pots, but only if you know what you’re doing. Strawberries are temperamental. They prefer space, cool soil, and food at all times of the year. When you grow strawberries in pots, you expose them to less space, warmer soil, and also fewer nutrients, all of which can reduce their yield. However, with a little more care it is possible to grow strawberries in pots to produce a rich harvest.
Benefits Of Growing Strawberries In Pots
Growing strawberries in a pot have a lot of distinct advantages. Plants can be adjusted to track the sun, allowing them to get more warmth and light than they would otherwise. They can be lifted off the ground to avoid slugs and avoid soil-borne diseases. Plants can also be moved under cover in the winter to force an early yield. It is possible to enjoy a much longer harvest from the same kind of strawberry by leaving some plants outside and others under the cover of a greenhouse or polytunnel.
Which Strawberry Varieties Can You Grow In Pots?
Garden Strawberries
Almost all varieties of strawberries will produce a good yield when grown in pots. Some varieties will produce a harvest just once a year, while others supply a continuous yield for several weeks.
Most of the time gardeners will choose a cultivar of the garden strawberry – Fragaria x ananassa. Fragaria x ananassa is the main strawberry type that is grown in gardens and in commercial cultivation. These types require a bright and light location, and will always fruit best in full sun.
Woodland / Wild / Alpine
You can also grow Fragaria vesca . it is also called woodland or ‘wild’ strawberries. Fragaria vesca ‘Semperflora’ L. is one type of wild strawberry, sometimes it is called the alpine strawberry. It produces little fruits, but they are believed to be more delicious than garden varieties.
One of the advantages of woodland/wild/alpine strawberries is that they may be cultivated in more shady areas. Even in light or dappled shade, they will bear fruit.
June-Bearing, Ever-bearing Or Day-Neutral
June-Bearing will all bear their fruits over a relatively short period around June or July (depending on climate and conditions). , Ever-bearing does have a longer period of harvesting.
What Are The Best Containers For Growing Strawberries?
Strawberries are excellent container fruits due to their compact and rapid growth, but they are equally at home in a dedicated bed. Hanging baskets, terracotta pots, and special strawberry planters are just a few of the containers in which you can grow them very well.
Growing Bags
The growing bag must be 95cm 35cm in size. It has a maximum capacity of 6 plants. You can use a conventional grow bag with holes. This is a low-cost method of growing strawberries. Growing bags protect fruits from slugs. However, this is not an attractive option because it requires a considerable amount of ground space.
Clay Window Box
A clay window box is a compact and slim container. It’s ideal for windows or a balcony. You can grow a maximum of four strawberry plants in it. Fill the window box with good potting soil. It’s important to fertilize your strawberry plants every 10 days. Use a water-soluble fertilizer (Eg;10-10-10 or 20-20-20). Maintain the frequency of watering to ensure that your plants grow.
Classic Strawberry Pot
Strawberry planters in terra cotta pots are typical. Strawberry plants can grow along the sides of large size containers since the sides have openings. The opening sides of the pots resemble small windows with a distinct appearance. Terracotta pots are made by using clay.
Hanging Baskets
These coir-lined wire baskets are large enough for 1-2 bushy strawberry plants and are supportive. Hanging Baskets allow strawberries to hang out in every direction and create a beautiful accessory that is both edible and ornamental.
Tips For Growing Strawberries In Pots Or Containers
1. Prepare The Plants
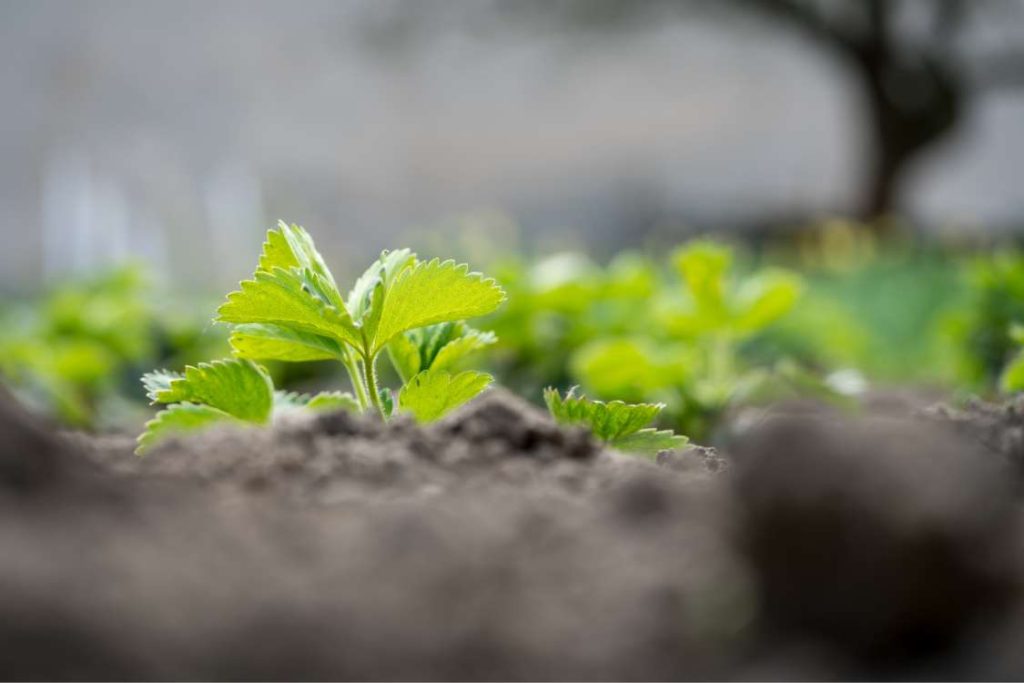

Strawberry planting can be started from transplants or bare-root crowns. Transplants will seem lush and attractive in containers, but dormant bare-root crowns will need time to develop and produce leaves. Strawberry plants dislike being overcrowded, so plant no more than three strawberry plants per square foot of soil. Because their roots are shallow, measure the container’s surface area to determine the area.
2. Add Soil
The containers are filled with a loose, loamy potting mix that will hold moisture but quickly drain away any excess water. Make sure to use a pot with a drainage hole in the bottom.
3. Plant the Strawberries
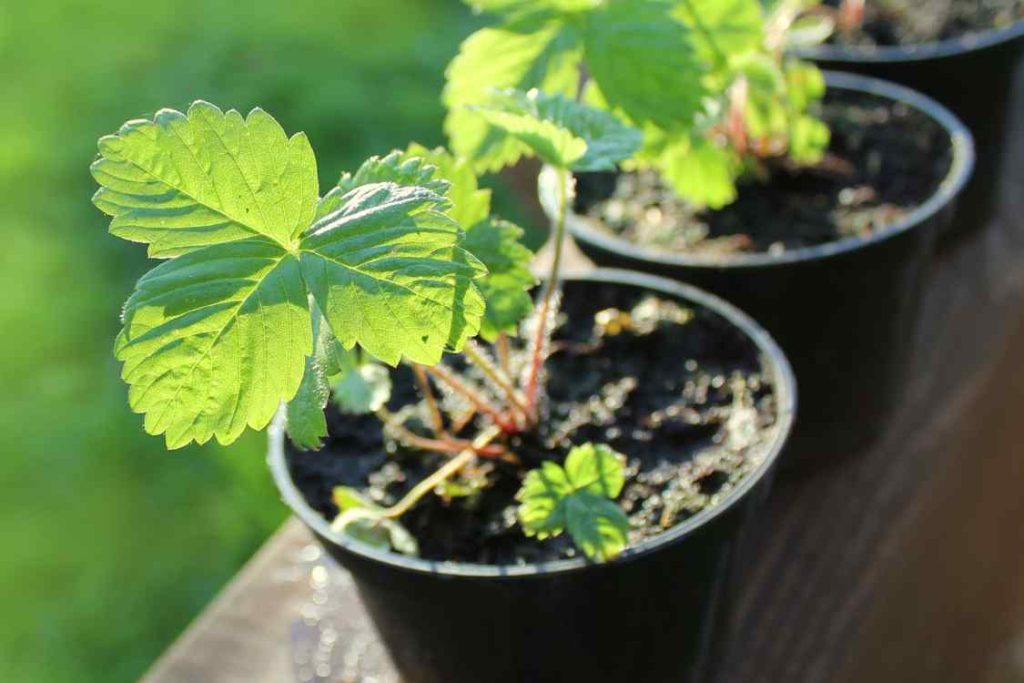

The strawberry plants are planted as their crowns are just above the soil surface. Then make a small mound in the potting mix. The potting mix is spread out the roots over the mound. The roots are covered up to the crown with the potting mix and water the soil well. Addition of more potting mix as needed after the soil settles from watering, but do not cover the crown with soil.
4. Place the Container
Set the pot in a spot that receives at least 8 to 12 hours of direct sunlight per day to ensure a plentiful supply of blooms and fruits. If the light is only coming from one direction, rotate the container every three to four days to ensure that the plants grow equally.
Also, make certain that the plants are well-protected. Pests can still reach the strawberries because they are in pots. Insects, birds, and rodents will continue to be attracted to your plants, so protect them with netting or fencing.
5. Mulching
A good layer of mulch is essential for healthy, productive strawberries. It helps the soil retain moisture, warm in the winter, and keeps the plants cool in the summer. It helps to keep the berries disease-free by providing a barrier between the fruit and any bacteria or pests in the soil. The best mulches for strawberries are pine needles, shredded leaves, or straw.
6. Water the Plants
Water your strawberries once a week or whenever the soil gets dry approximately 1 inch below the surface. You don’t want water or moist soil around the plants. In order to give the optimal environment for fruits to form, keep the soil slightly damp but not dry or waterlogged. The soil in pots dries out faster than the soil on the ground. As a result, extended periods of hot, dry weather may require twice-daily watering.
7. Fertilize Regularly
Feed your strawberry plants every other week with a potassium-rich liquid fertilizer to promote fruit production or a balanced 10-10-10 or its organic equivalent for general plant health. After applying the granules, brush them off the leaves.
8. Protect From Disease
When the fruits start to form, gently move them off the ground by tucking straw or wood chips underneath. This reduces the risk of disease.
9. Harvesting
You may just get one harvest or many throughout the summer, depending on the variety of strawberries you grow in your pots. Cut the stem just above the fruit to remove the strawberries after they have become fully red.
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024
- 10 Stunning Canopy Bed Ideas for a Dreamy Escape - May 16, 2024