Unveiling the Secrets: Money Plant Diseases and How To Cure Them
Houseplants are become a common element in décor. Interior designers create must-have palettes of houseplants in the same way that they choose paint colors. In particular, money trees are a beloved and well-liked option.
They are beloved by novice plant gardeners as well as by hungry insects. When you first bring your Money Tree home, you might be curious about how many diseases can affect your money plant. Let’s see what are those common money plant diseases.
1. Root Rot

Improper and irregular watering makes all three money plants susceptible to root rot. Over- and under-watering weakens the root systems of each plant, which causes the roots to become susceptible to the natural fungi present in its soil.
The jade plant is a highly drought-tolerant succulent that requires slightly dry soils. Over-watering will quickly rot the roots of this plant. Both the honesty plant and Guiana chestnut need continuously moist but not saturated soils.
While these money plants will tolerate an occasional over-watering, frequent overwatering will waterlog the soils and promote root rot infections. To prevent this disease, money plants should be watered only according to their individual needs rather than on a schedule.
Read – DIY Automatic Watering System For Indoor Plants
- Improper and irregular watering makes all three money plants susceptible to root rot.
- While these money plants will tolerate an occasional over-watering, frequent overwatering will waterlog the soils and promote root rot infections.
2. Bacterial Wilt Disease
Causing Agent: Pseudomonas cichorii
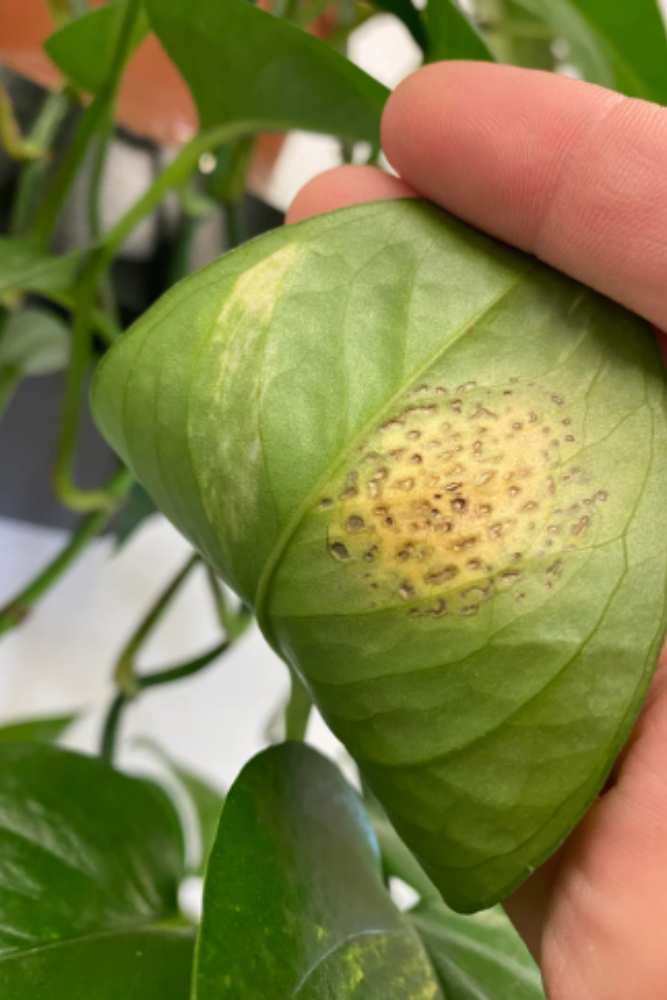

The veins in the leaves and stems get darker as a result of this disease. The leaves begin to droop and quickly spread yellow patches.
Repot the plant in new soil and a fresh container after discarding the diseased components. Use a potting mix that is well-draining and porous, and avoid overwatering the money plant.
3. Leaf Spot
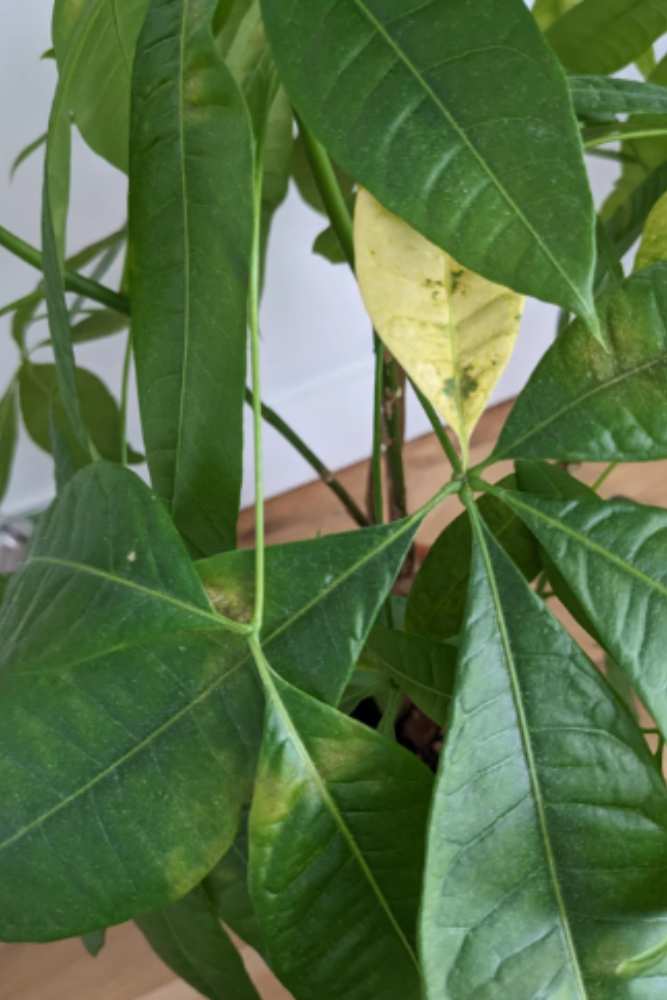

All plants and trees, including each money plant, are susceptible to at least one variation of leaf spot disease. Leaf spot diseases can be fungal or bacterial. These spore-borne diseases cause small, necrotic spots on the foliage that enlarge with the disease’s progression.
The spots are often encircled with reddish or yellowish outlines, and the infected leaves often become discolored. The infection causes the leaves to wilt, and severely infected plants often experience dieback, growth stunt, and premature defoliation.
Leaf spot infections can be controlled by removing the infected leaves and keeping the money plant’s area free of debris and defoliation.
- All plants and trees, including each money plant, are susceptible to at least one variation of leaf spot disease.
- Leaf spot infections can be controlled by removing the infected leaves and keeping the money plant’s area free of debris and defoliation.
4. White Rust

Cause The fungus-like organism Albugo candida has been found in a commercial operation in Oregon and in gardens in Washington and Oregon. Dew, fog, or periods of extended rainfall and cool temperatures favor disease development. Other hosts include canola, horseradish, and radish.
Symptoms: White to cream-colored, blister-like lesions on leaves and siliques. Infected production plants were stunted and had overall poor growth.
Cultural Control
- Select fields away from established radish fields.
- Control wild mustards around the field.
- Incorporate plant debris into soil soon after harvest.
5. Powdery Mildew
There is a variety of different fungal variations that create the powdery mildew disease. Each variation infects its own collection of hosts, including annual and perennial flowers and deciduous and evergreen trees and vegetation.
Powdery mildew infects all three variations of the money plant, especially the succulent jade, which is the most susceptible of the three. This spore-borne infection attacks the foliage of the plant, causing small necrotic spots on the leaves that are covered by a powdery white fungal covering.
Powdery mildew infections are most aggressive during the warm, dry periods that are accompanied by high humidity levels. Still, the infection is relatively easy to treat when addressed early in the infection.
- There is a variety of different fungal variations that create the powdery mildew disease.
- This spore-borne infection attacks the foliage of the plant, causing small necrotic spots on the leaves that are covered by a powdery white fungal covering.
Related Posts
- Brown Spots on Indoor Cactus
- Chinese Money Plant White Spots
- How to Treat Fungus on Succulents
- Chinese Evergreen Brown Spots
- Monstera Leaf Spot Disease
- Brown Spots on outdoor Plant Leaves
- 29 Bucket Gardening Ideas for a Lush, Compact Garden - October 30, 2024
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024