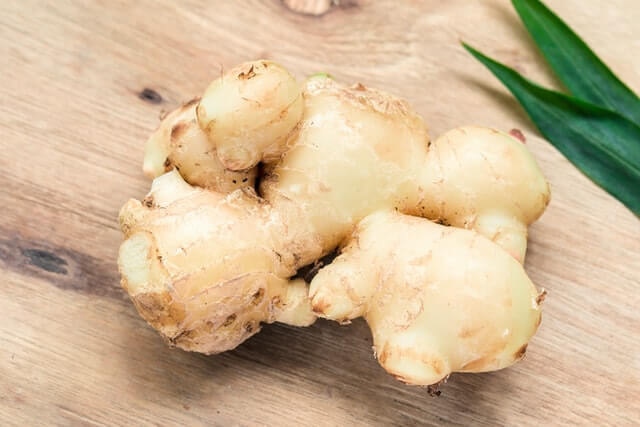
Root and Tuber Crops
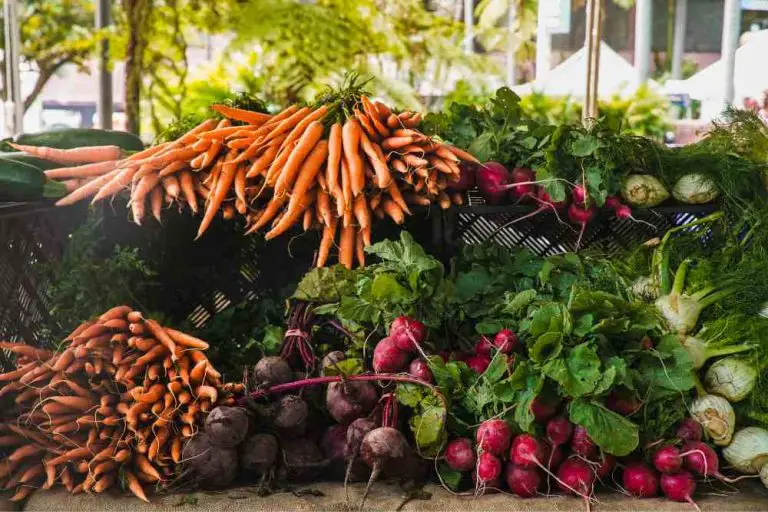
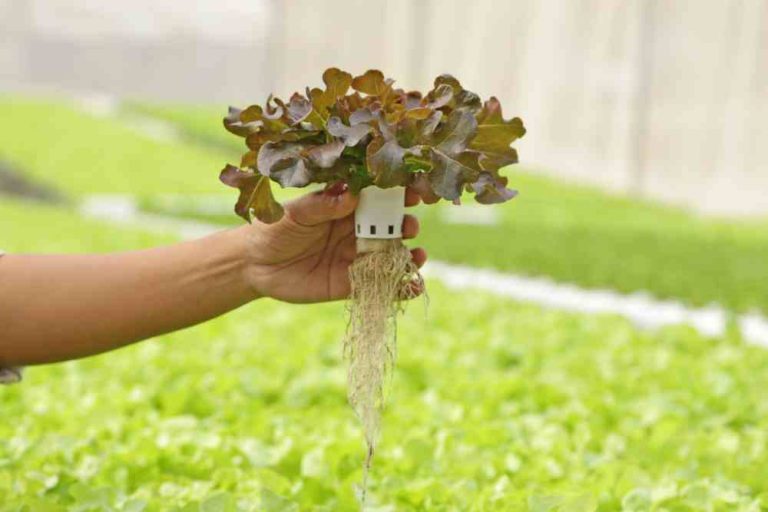
Any plant with an edible underground storage organ is known as a root and tuber crops. It can be divided into two parts namely modified root and modified stem. Again modified roots can be divided into two parts; taproots and adventitious roots. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes. The node holds one…