Choosing the Best Compost for House Plants – A Gardener’s Guide
All of us have heard about the fantastic advantages of using compost in the garden. It fosters plant growth and enhances the condition of the soil. But what about the plants in an indoor garden? Can indoor plants be composted?
Choosing the best compost for house plants is essential if you want your indoor plants to be vigorous and flourish for years. Potting your houseplant in the wrong growing medium can cause it to become ill or even die. If you need help choosing the best plant compost, this article can point you in the right direction.
Both outdoor and indoor plants benefit from the great versatility of compost as an organic soil additive. In addition to not harming your houseplants, it won’t introduce any unpleasant odors inside. This article describes why compost benefits indoor plants, whether a specific type of compost is required, and how to utilize compost efficiently for houseplants.
Compost For Houseplants
The most obvious and well-liked choice is the compost for houseplants that you can get in supermarkets. These will ensure that your indoor plants are provided with the nutrients, a well-drained substrate, and a bag that will make storing simple that they need. In addition to standard, all-purpose compost, there are specific blends for ferns, cacti & succulents, aroids, carnivorous plants, and a variety of other plants.
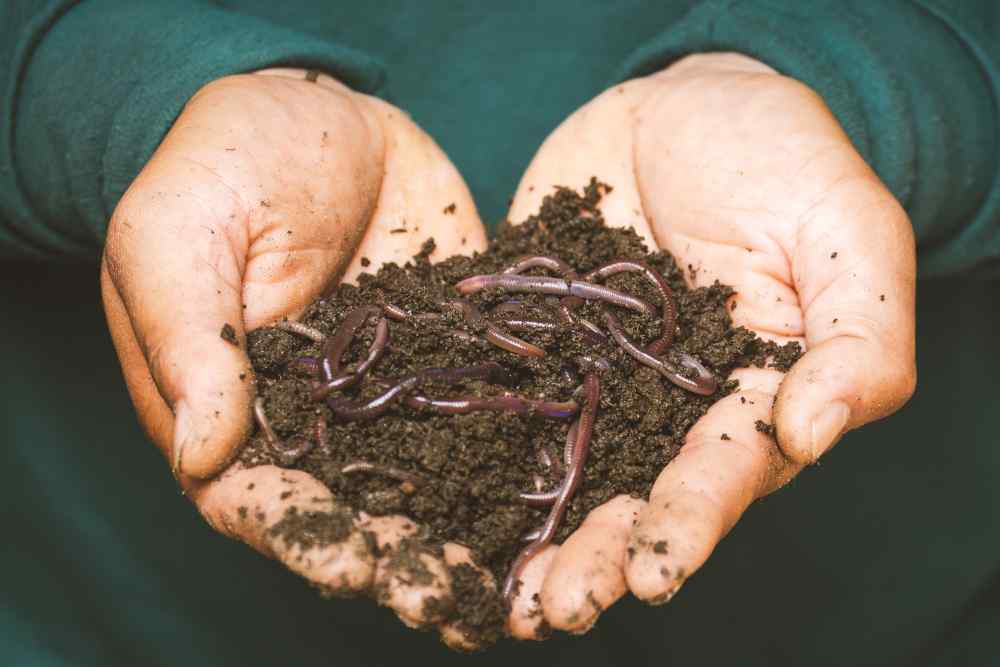

Animal manure, decaying food scraps, lawn clippings, garden waste, insects, worms, and microorganisms are among the other things found in compost that you wouldn’t want inside your house. So some people who grow plants indoors are apprehensive about using compost for their plants. But if compost is made correctly, it shouldn’t smell bad. The health of the soil and plants can both greatly benefit from compost. Both indoor and outdoor garden plants can use it!
Types Of Compost For Indoor Plants
Where you wish to live is something you consider carefully. And you must take the same care as a responsible plant parent with anything you place in a plant pot! Compost for indoor plants comes in a variety of forms, from general to specialized. The most common ones include:
- Bio-compost, which is formed from food waste and contains a massive amount of nutrients.
- Compost for plants that prefer acidic soil, such as asters, begonias, and coleus.
- Cactus compost, Cacti prefer alkaline soil to grow. The alkaline, nutrient-rich cactus compost is ideal for growing healthy plants.
- Flower compost, which is a multipurpose compost suitable for most plants. It serves as an excellent all-purpose compost for houseplants.
- Organic potting mix, a compost that can be used for all types of potted plants. Vermiculite, perlite, and compost are frequently used in conjunction.
- Potting compost is compost made specifically for plants in pots.
How To Use Compost On Houseplants In Pots?
Composting indoor potted plants is a simple process. The following three methods will assist your plants in gaining the advantages of compost:
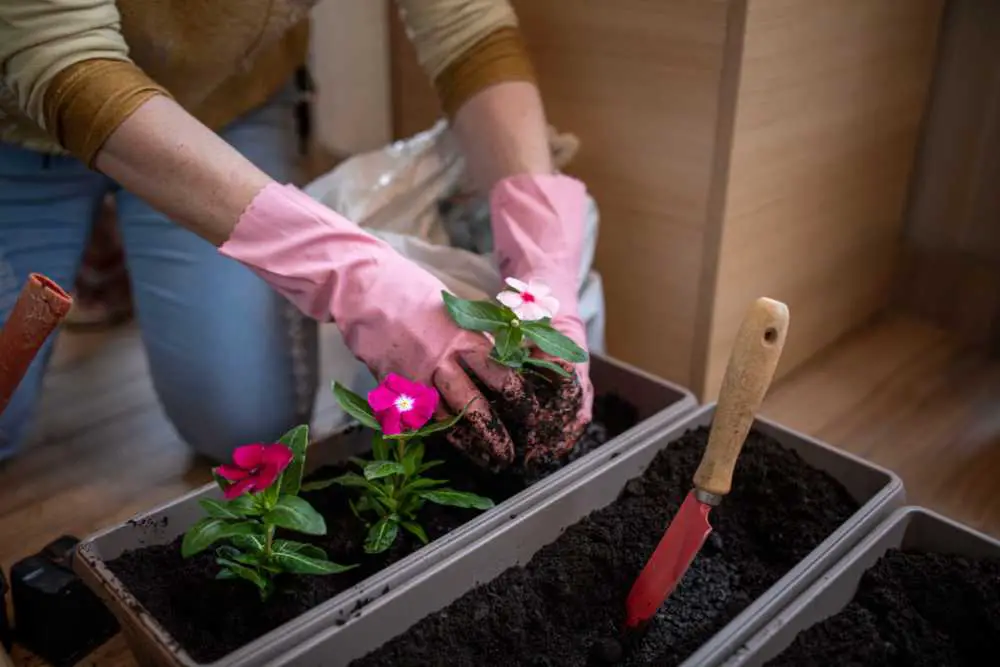
When potting and repotting plants, incorporate compost into the soil mixture. Approximately one-third of the potting soil should be composted. Using more than this can cause soil problems. Compost should be added to each pot by about 1 inch. It is not necessary to incorporate the layer into the soil. After scattering it on the soil’s surface, give the plants a good watering. Making a “tea” for your houseplants can be done with worm castings or compost from a compost heap. To feed your plants, combine the compost and water in a bucket, let it stand for 24 hours, and then filter the mixture.
How Frequently Should Compost Be Added To Indoor Plants?
Depending on the compost you use and the kinds of indoor plants you have, you may need to add compost to them more frequently. You only need to replenish your pots once or twice a year if you use compost from a heap or mushroom compost. Just once a year is plenty for plants like cactus that prefer sandier soil. If using vermicompost, add a little bit to each pot once a month or every three months.
Can Potted Plants Use Too Much Compost?
A maximum amount of compost should be used for indoor potted plants. Excess fertilizers might burn your plants’ roots and turn their leaves brown if you use too much of them. Therefore, You should ensure that compost makes up no more than around a one – third of the growing soil in a container.
The Best Compost For Houseplants
To respond to this question, we should consider some of the essential elements that indoor plants require to thrive: To avoid compaction and root rot, the soil must be adequately aerated and well drained. Nutrient forms that are easy for plants to absorb include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Soil that has the proper pH for the specific plant species. The finished compost from a compost heap is full of nutrients and bacteria, but depending on how it was formed, it may have a texture that is too fine for houseplants in pots. Similar principles frequently apply to mushroom compost. Using too fine compost might cause drainage problems for indoor plants since it makes the soil too compact.
On the other hand, plants with aerial roots, such as aroids and orchids, do very well in coarse-textured compost. Although vermicompost has a finer texture than the other two varieties of compost, it functions differently. Worm castings enhance the soil’s texture by improving drainage and aeration. Even though worm compost is nutrient-rich, the roots of plants cannot be burned by it since the nutrients are released to the plant very gradually. Worm castings are also excellent for adjusting the pH of the soil. Since they have a pH of 7, they help prevent soil from becoming overly acidic or alkaline. Worm castings are the best compost you can use for your houseplants.
Repotting Houseplants: The Best Compost Repotting indoor plants will provide them with a fresh supply of nutrients and organic matter while renewing their growing material. Compost should always be included in the potting mixture. But which kind of compost is ideal for repotting your houseplants?
This can be accomplished using composted mushrooms and worm castings. However, many indoor gardeners discover that their plants require more nutrients to grow. The best compost for repotting is finished compost from a compost heap. The soil’s ability to retain water is enhanced by its extremely high level of organic matter. Additionally, as it decomposes, nutrients are gradually released to plants.
- 29 Bucket Gardening Ideas for a Lush, Compact Garden - October 30, 2024
- 20+ Chic Boho Bedroom Ideas for a Cozy and Stylish Retreat - June 20, 2024
- 12+ Modern Boho Living Room Ideas to Create a Unique Oasis - June 10, 2024